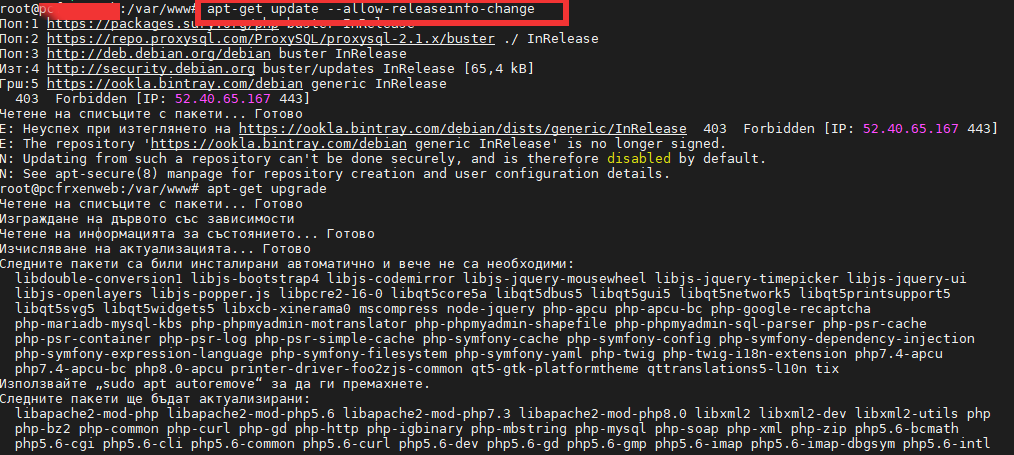
Here is the scenario, lets say you have on your daily task list two Hypervisor (HV) hosts running CentOS or RHEL Linux with KVM or Virutozzo technology and inside the HV hosts you have configured at least 2 pairs of virtual machines one residing on HV Host 1 and one residing on HV Host 2 and you need to constantly keep the hosts to the latest distribution major release security patchset.
The Virtual Machines has been running another set of Redhat Linux or CentOS configured to work in a High Availability Cluster running Haproxy / Apache / Postfix or any other kind of HA solution on top of corosync / keepalived or whatever application cluster scripts Free or Open Source technology that supports a switch between clustered Application nodes.
The logical question comes how to keep up the CentOS / RHEL Machines uptodate without interfering with the operations of the Applications running on the cluster?
Assuming that the 2 or more machines are configured to run in Active / Passive App member mode, e.g. one machine is Active at any time and the other is always Passive, a switch is possible between the Active and Passive node.

In this article I'll give a simple step by step tested example on how you I succeeded to update (for security reasons) up to the latest available Distribution major release patchset on one by one first the Clustered App on Virtual Machines 1 and VM2 on Linux Hypervisor Host 1. Then the App cluster VM 1 / VM 2 on Hypervisor Host 2.
And finally update the Hypervisor1 (after moving the Active resources from it to Hypervisor2) and updating the Hypervisor2 after moving the App running resources back on HV1.
I know the procedure is a bit monotonic but it tries to go through everything step by step to try to mitigate any possible problems. In case of failure of some rpm dependencies during yum / dnf tool updates you can always revert to backups so in anyways don't forget to have a fully functional backup of each of the HV hosts and the VMs somewhere on a separate machine before proceeding further, any possible failures due to following my aritcle literally is your responsibility 🙂
0. Check situation before the update on HVs / get VM IDs etc.
Check the virsion of each of the machines to be updated both Hypervisor and Hosted VMs, on each machine run:
# cat /etc/redhat-release
CentOS Linux release 7.9.2009 (Core)
The machine setup I'll be dealing with is as follows:
hypervisor-host1 -> hypervisor-host1.fqdn.com
• virt-mach-centos1
• virt-machine-zabbix-proxy-centos (zabbix proxy)
hypervisor-host2 -> hypervisor-host2.fqdn.com
• virt-mach-centos2
• virt-machine-zabbix2-proxy-centos (zabbix proxy)
To check what is yours check out with virsh cmd –if on KVM or with prlctl if using Virutozzo, you should get something like:
[root@hypervisor-host2 ~]# virsh list
Id Name State
—————————————————-
1 vm-host1 running
2 virt-mach-centos2 running
# virsh list –all
[root@hypervisor-host1 ~]# virsh list
Id Name State
—————————————————-
1 vm-host2 running
3 virt-mach-centos1 running
[root@hypervisor-host1 ~]# prlctl list
UUID STATUS IP_ADDR T NAME
{dc37c201-08c9-589d-aa20-9386d63ce3f3} running – VM virt-mach-centos1
{76e8a5f8-caa8-5442-830e-aa4bfe8d42d9} running – VM vm-host2
[root@hypervisor-host1 ~]#
If you have stopped VMs with Virtuozzo to list the stopped ones as well.
# prlctl list -a
[root@hypervisor-host2 74a7bbe8-9245-5385-ac0d-d10299100789]# vzlist -a
CTID NPROC STATUS IP_ADDR HOSTNAME
[root@hypervisor-host2 74a7bbe8-9245-5385-ac0d-d10299100789]# prlctl list
UUID STATUS IP_ADDR T NAME
{92075803-a4ce-5ec0-a3d8-9ee83d85fc76} running – VM virt-mach-centos2
{74a7bbe8-9245-5385-ac0d-d10299100789} running – VM vm-host1
# prlctl list -a
If due to Virtuozzo version above command does not return you can manually check in the VM located folder, VM ID etc.
[root@hypervisor-host2 vmprivate]# ls
74a7bbe8-9245-4385-ac0d-d10299100789 92075803-a4ce-4ec0-a3d8-9ee83d85fc76
[root@hypervisor-host2 vmprivate]# pwd
/vz/vmprivate
[root@hypervisor-host2 vmprivate]#
[root@hypervisor-host1 ~]# ls -al /vz/vmprivate/
total 20
drwxr-x—. 5 root root 4096 Feb 14 2019 .
drwxr-xr-x. 7 root root 4096 Feb 13 2019 ..
drwxr-x–x. 4 root root 4096 Feb 18 2019 1c863dfc-1deb-493c-820f-3005a0457627
drwxr-x–x. 4 root root 4096 Feb 14 2019 76e8a5f8-caa8-4442-830e-aa4bfe8d42d9
drwxr-x–x. 4 root root 4096 Feb 14 2019 dc37c201-08c9-489d-aa20-9386d63ce3f3
[root@hypervisor-host1 ~]#
Before doing anything with the VMs, also don't forget to check the Hypervisor hosts has enough space, otherwise you'll get in big troubles !
[root@hypervisor-host2 vmprivate]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/centos_hypervisor-host2-root 20G 1.8G 17G 10% /
devtmpfs 20G 0 20G 0% /dev
tmpfs 20G 0 20G 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 20G 2.0G 18G 11% /run
tmpfs 20G 0 20G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda1 992M 159M 766M 18% /boot
/dev/mapper/centos_hypervisor-host2-home 9.8G 37M 9.2G 1% /home
/dev/mapper/centos_hypervisor-host2-var 9.8G 355M 8.9G 4% /var
/dev/mapper/centos_hypervisor-host2-vz 755G 25G 692G 4% /vz
[root@hypervisor-host1 ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/centos-root 50G 1.8G 45G 4% /
devtmpfs 20G 0 20G 0% /dev
tmpfs 20G 0 20G 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 20G 2.1G 18G 11% /run
tmpfs 20G 0 20G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda2 992M 153M 772M 17% /boot
/dev/mapper/centos-home 9.8G 37M 9.2G 1% /home
/dev/mapper/centos-var 9.8G 406M 8.9G 5% /var
/dev/mapper/centos-vz 689G 12G 643G 2% /vz
Another thing to do before proceeding with update is to check and tune if needed the amount of CentOS repositories used, before doing anything with yum.
[root@hypervisor-host2 yum.repos.d]# ls -al
total 68
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 Oct 6 13:13 .
drwxr-xr-x. 110 root root 12288 Oct 7 11:13 ..
-rw-r–r–. 1 root root 4382 Mar 14 2019 CentOS7.repo
-rw-r–r–. 1 root root 1664 Sep 5 2019 CentOS-Base.repo
-rw-r–r–. 1 root root 1309 Sep 5 2019 CentOS-CR.repo
-rw-r–r–. 1 root root 649 Sep 5 2019 CentOS-Debuginfo.repo
-rw-r–r–. 1 root root 314 Sep 5 2019 CentOS-fasttrack.repo
-rw-r–r–. 1 root root 630 Sep 5 2019 CentOS-Media.repo
-rw-r–r–. 1 root root 1331 Sep 5 2019 CentOS-Sources.repo
-rw-r–r–. 1 root root 6639 Sep 5 2019 CentOS-Vault.repo
-rw-r–r–. 1 root root 1303 Mar 14 2019 factory.repo
-rw-r–r–. 1 root root 666 Sep 8 10:13 openvz.repo
[root@hypervisor-host2 yum.repos.d]#
[root@hypervisor-host1 yum.repos.d]# ls -al
total 68
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 Oct 6 13:13 .
drwxr-xr-x. 112 root root 12288 Oct 7 11:09 ..
-rw-r–r–. 1 root root 1664 Sep 5 2019 CentOS-Base.repo
-rw-r–r–. 1 root root 1309 Sep 5 2019 CentOS-CR.repo
-rw-r–r–. 1 root root 649 Sep 5 2019 CentOS-Debuginfo.repo
-rw-r–r–. 1 root root 314 Sep 5 2019 CentOS-fasttrack.repo
-rw-r–r–. 1 root root 630 Sep 5 2019 CentOS-Media.repo
-rw-r–r–. 1 root root 1331 Sep 5 2019 CentOS-Sources.repo
-rw-r–r–. 1 root root 6639 Sep 5 2019 CentOS-Vault.repo
-rw-r–r–. 1 root root 1303 Mar 14 2019 factory.repo
-rw-r–r–. 1 root root 300 Mar 14 2019 obsoleted_tmpls.repo
-rw-r–r–. 1 root root 666 Sep 8 10:13 openvz.repo
1. Dump VM definition XMs (to have it in case if it gets wiped during update)
There is always a possibility that something will fail during the update and you might be unable to restore back to the old version of the Virtual Machine due to some config misconfigurations or whatever thus a very good idea, before proceeding to modify the working VMs is to use KVM's virsh and dump the exact set of XML configuration that makes the VM roll properly.
To do so:
Check a little bit up in the article how we have listed the IDs that are part of the directory containing the VM.
[root@hypervisor-host1 ]# virsh dumpxml (Id of VM virt-mach-centos1 ) > /root/virt-mach-centos1_config_bak.xml
[root@hypervisor-host2 ]# virsh dumpxml (Id of VM virt-mach-centos2) > /root/virt-mach-centos2_config_bak.xml
2. Set on standby virt-mach-centos1 (virt-mach-centos1)
As I'm upgrading two machines that are configured to run an haproxy corosync cluster, before proceeding to update the active host, we have to switch off
the proxied traffic from node1 to node2, – e.g. standby the active node, so the cluster can move up the traffic to other available node.
[root@virt-mach-centos1 ~]# pcs cluster standby virt-mach-centos1
3. Stop VM virt-mach-centos1 & backup on Hypervisor host (hypervisor-host1) for VM1
Another prevention step to make sure you don't get into damaged VM or broken haproxy cluster after the upgrade is to of course backup
[root@hypervisor-host1 ]# prlctl backup virt-mach-centos1
or
[root@hypervisor-host1 ]# prlctl stop virt-mach-centos1
[root@hypervisor-host1 ]# cp -rpf /vz/vmprivate/dc37c201-08c9-489d-aa20-9386d63ce3f3 /vz/vmprivate/dc37c201-08c9-489d-aa20-9386d63ce3f3-bak
[root@hypervisor-host1 ]# tar -czvf virt-mach-centos1_vm_virt-mach-centos1.tar.gz /vz/vmprivate/dc37c201-08c9-489d-aa20-9386d63ce3f3
[root@hypervisor-host1 ]# prlctl start virt-mach-centos1
4. Remove package version locks on all hosts
If you're using package locking to prevent some other colleague to not accidently upgrade the machine (if multiple sysadmins are managing the host), you might use the RPM package locking meachanism, if that is used check RPM packs that are locked and release the locking.
+ List actual list of locked packages
[root@hypervisor-host1 ]# yum versionlock list
…
…..
0:libtalloc-2.1.16-1.el7.*
0:libedit-3.0-12.20121213cvs.el7.*
0:p11-kit-trust-0.23.5-3.el7.*
1:quota-nls-4.01-19.el7.*
0:perl-Exporter-5.68-3.el7.*
0:sudo-1.8.23-9.el7.*
0:libxslt-1.1.28-5.el7.*
versionlock list done
+ Clear the locking
# yum versionlock clear
+ List actual list / == clear all entries
[root@virt-mach-centos2 ]# yum versionlock list; yum versionlock clear
[root@virt-mach-centos1 ]# yum versionlock list; yum versionlock clear
[root@hypervisor-host1 ~]# yum versionlock list; yum versionlock clear
[root@hypervisor-host2 ~]# yum versionlock list; yum versionlock clear
5. Do yum update virt-mach-centos1
For some clarity if something goes wrong, it is really a good idea to make a dump of the basic packages installed before the RPM package update is initiated,
The exact versoin of RHEL or CentOS as well as the list of locked packages, if locking is used.
Enter virt-mach-centos1 (ssh virt-mach-centos1) and run following cmds:
# cat /etc/redhat-release > /root/logs/redhat-release-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
# cat /etc/grub.d/30_os-prober > /root/logs/grub2-efi-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
+ Only if needed!!
# yum versionlock clear
# yum versionlock list
Clear any previous RPM packages – careful with that as you might want to keep the old RPMs, if unsure comment out below line
# yum clean all |tee /root/logs/yumcleanall-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
Proceed with the update and monitor closely the output of commands and log out everything inside files using a small script that you should place under /root/status the script is given at the end of the aritcle.:
yum check-update |tee /root/logs/yumcheckupdate-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
yum check-update | wc -l
yum update |tee /root/logs/yumupdate-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
sh /root/status |tee /root/logs/status-before-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
6. Check if everything is running fine after upgrade
Reboot VM
# shutdown -r now
7. Stop VM virt-mach-centos2 & backup on Hypervisor host (hypervisor-host2)
Same backup step as prior
# prlctl backup virt-mach-centos2
or
# prlctl stop virt-mach-centos2
# cp -rpf /vz/vmprivate/92075803-a4ce-4ec0-a3d8-9ee83d85fc76 /vz/vmprivate/92075803-a4ce-4ec0-a3d8-9ee83d85fc76-bak
## tar -czvf virt-mach-centos2_vm_virt-mach-centos2.tar.gz /vz/vmprivate/92075803-a4ce-4ec0-a3d8-9ee83d85fc76
# prctl start virt-mach-centos2
8. Do yum update on virt-mach-centos2
Log system state, before the update
# cat /etc/redhat-release > /root/logs/redhat-release-vorher-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
# cat /etc/grub.d/30_os-prober > /root/logs/grub2-efi-vorher-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
# yum versionlock clear == if needed!!
# yum versionlock list
+ Clean old install update / packages if required
# yum clean all |tee /root/logs/yumcleanall-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
Initiate the update
# yum check-update |tee /root/logs/yumcheckupdate-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out 2>&1
# yum check-update | wc -l
# yum update |tee /root/logs/yumupdate-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out 2>&1
# sh /root/status |tee /root/logs/status-before-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
9. Check if everything is running fine after upgrade
Reboot VM
# shutdown -r now
10. Stop VM vm-host2 & backup
# prlctl backup vm-host2
or
# prlctl stop vm-host2
Or copy the actual directory containig the Virtozzo VM (use the correct ID)
# cp -rpf /vz/vmprivate/76e8a5f8-caa8-5442-830e-aa4bfe8d42d9 /vz/vmprivate/76e8a5f8-caa8-5442-830e-aa4bfe8d42d9-bak
## tar -czvf vm-host2.tar.gz /vz/vmprivate/76e8a5f8-caa8-4442-830e-aa5bfe8d42d9
# prctl start vm-host2
11. Do yum update vm-host2
# cat /etc/redhat-release > /root/logs/redhat-release-vorher-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
# cat /etc/grub.d/30_os-prober > /root/logs/grub2-efi-vorher-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
Clear only if needed
# yum versionlock clear
# yum versionlock list
# yum clean all |tee /root/logs/yumcleanall-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
Do the rpm upgrade
# yum check-update |tee /root/logs/yumcheckupdate-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
# yum check-update | wc -l
# yum update |tee /root/logs/yumupdate-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
# sh /root/status |tee /root/logs/status-before-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
12. Check if everything is running fine after upgrade
Reboot VM
# shutdown -r now
13. Do yum update hypervisor-host2
# cat /etc/redhat-release > /root/logs/redhat-release-vorher-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
# cat /etc/grub.d/30_os-prober > /root/logs/grub2-efi-vorher-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
Clear lock if needed
# yum versionlock clear
# yum versionlock list
# yum clean all |tee /root/logs/yumcleanall-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
Update rpms
# yum check-update |tee /root/logs/yumcheckupdate-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out 2>&1
# yum check-update | wc -l
# yum update |tee /root/logs/yumupdate-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out 2>&1
# sh /root/status |tee /root/logs/status-before-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
14. Stop VM vm-host1 & backup
Some as ealier
# prlctl backup vm-host1
or
# prlctl stop vm-host1
# cp -rpf /vz/vmprivate/74a7bbe8-9245-4385-ac0d-d10299100789 /vz/vmprivate/74a7bbe8-9245-4385-ac0d-d10299100789-bak
# tar -czvf vm-host1.tar.gz /vz/vmprivate/74a7bbe8-9245-4385-ac0d-d10299100789
# prctl start vm-host1
15. Do yum update vm-host2
# cat /etc/redhat-release > /root/logs/redhat-release-vorher-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
# cat /etc/grub.d/30_os-prober > /root/logs/grub2-efi-vorher-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
# yum versionlock clear == if needed!!
# yum versionlock list
# yum clean all |tee /root/logs/yumcleanall-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
# yum check-update |tee /root/logs/yumcheckupdate-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
# yum check-update | wc -l
# yum update |tee /root/logs/yumupdate-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
# sh /root/status |tee /root/logs/status-before-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
16. Check if everything is running fine after upgrade
+ Reboot VM
# shutdown -r now
17. Do yum update hypervisor-host1
Same procedure for HV host 1
# cat /etc/redhat-release > /root/logs/redhat-release-vorher-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
# cat /etc/grub.d/30_os-prober > /root/logs/grub2-efi-vorher-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
Clear lock
# yum versionlock clear
# yum versionlock list
# yum clean all |tee /root/logs/yumcleanall-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
# yum check-update |tee /root/logs/yumcheckupdate-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
# yum check-update | wc -l
# yum update |tee /root/logs/yumupdate-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
# sh /root/status |tee /root/logs/status-before-$(hostname)-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S').out
18. Check if everything is running fine after upgrade
Reboot VM
# shutdown -r now
Check hypervisor-host1 all VMs run as expected
19. Check if everything is running fine after upgrade
Reboot VM
# shutdown -r now
Check hypervisor-host2 all VMs run as expected afterwards
20. Check once more VMs and haproxy or any other contained services in VMs run as expected
Login to hosts and check processes and logs for errors etc.
21. Haproxy Unstandby virt-mach-centos1
Assuming that the virt-mach-centos1 and virt-mach-centos2 are running a Haproxy / corosync cluster you can try to standby node1 and check the result
hopefully all should be fine and traffic should come to host node2.
[root@virt-mach-centos1 ~]# pcs cluster unstandby virt-mach-centos1
Monitor logs and make sure HAproxy works fine on virt-mach-centos1
22. If necessery to redefine VMs (in case they disappear from virsh) or virtuosso is not working
[root@virt-mach-centos1 ]# virsh define /root/virt-mach-centos1_config_bak.xml
[root@virt-mach-centos1 ]# virsh define /root/virt-mach-centos2_config_bak.xml
23. Set versionlock to RPMs to prevent accident updates and check OS version release
[root@virt-mach-centos2 ]# yum versionlock \*
[root@virt-mach-centos1 ]# yum versionlock \*
[root@hypervisor-host1 ~]# yum versionlock \*
[root@hypervisor-host2 ~]# yum versionlock \*
[root@hypervisor-host2 ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release
CentOS Linux release 7.8.2003 (Core)
Other useful hints
[root@hypervisor-host1 ~]# virsh console dc37c201-08c9-489d-aa20-9386d63ce3f3
Connected to domain virt-mach-centos1
..
! Compare packages count before the upgrade on each of the supposable identical VMs and HVs – if there is difference in package count review what kind of packages are different and try to make the machines to look as identical as possible !
Packages to update on hypervisor-host1 Count: XXX
Packages to update on hypervisor-host2 Count: XXX
Packages to update virt-mach-centos1 Count: – 254
Packages to update virt-mach-centos2 Count: – 249
The /root/status script
+++
#!/bin/sh
echo '======================================================= '
echo '= Systemctl list-unit-files –type=service | grep enabled '
echo '======================================================= '
systemctl list-unit-files –type=service | grep enabled
echo '======================================================= '
echo '= systemctl | grep ".service" | grep "running" '
echo '======================================================= '
systemctl | grep ".service" | grep "running"
echo '======================================================= '
echo '= chkconfig –list '
echo '======================================================= '
chkconfig –list
echo '======================================================= '
echo '= netstat -tulpn '
echo '======================================================= '
netstat -tulpn
echo '======================================================= '
echo '= netstat -r '
echo '======================================================= '
netstat -r
+++
That's all folks, once going through the article, after some 2 hours of efforts or so you should have an up2date machines.
Any problems faced or feedback is mostly welcome as this might help others who have the same setup.
Thanks for reading me 🙂