
If you've been given a new dedicated server from a New Dedicated-Server-Provider or VPS with Linux and you were told that a certain download speed to the Server is guaranteed from the server provider, in order to be sure the server's connection to the Internet told by service provider is correct it is useful to run a simple measurement console test after logging in remotely to the server via SSH.
Testing connection from Terminal is useful because as you probably know most of Linux / UNIX servers doesn't have a GUI interface and thus it is not possible to test Internet Up / Down Bandwidth through speedtest.net.
1. Testing Download Internet Speed given by ISP / Dedi-Server Provider from Linux Console
For the download speed (internet) test the historical approach was to just try downloading the Linux kernel source code from www.kernel.org with some text browser such as lynx or links count the seconds for which the download is completed and then multiple the kernel source archive size on the seconds to get an approximate bandwidth per second, however as nowdays internet connection speeds are much higher, thus it is better to try to download some Linux distribution iso file, you can still use kernel tar archive but it completed too fast to give you some good (adequate) statistics on Download bandwidth.
If its a fresh installed Linux server probably you will probably not have links / elinks and lynx text internet browers installed so install them depending on deb / rpm distro with:
If on Deb Linuz distro:
root@pcfreak:/root# apt-get install –yes links elinks lynx
…
On RPM Based Linuz distro:
[root@fedora ~]# yum install -y lynx elinks links
…
Conduct Internet Download Speed with links
root@pcfreak:/root# links https://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v3.x/linux-3.19.1.tar.xz
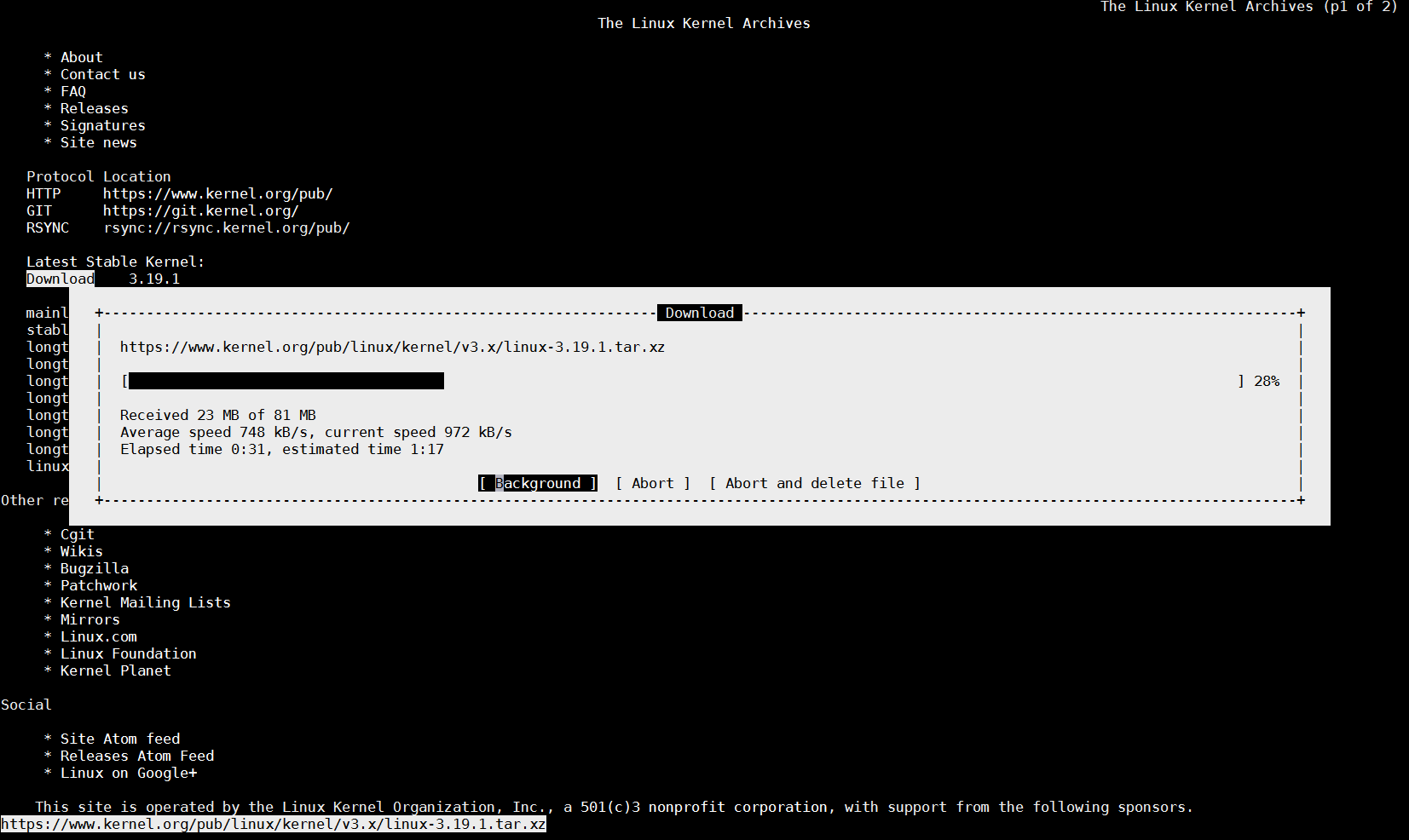
(Note that the kernel link is current latest stable Kernel source code archive in future that might change, so try with latest archive.)
You can also use non-interactive tool such as wget, curl or lftp to measure internet download speed
To test Download Internet Speed with wget without saving anything to disk set output to go to /dev/null
root@pcfreak:~# wget -O /dev/null https://www.pc-freak.net//~hipo/hirens-bootcd/HirensBootCD15/Hirens.BootCD.15.0.zip
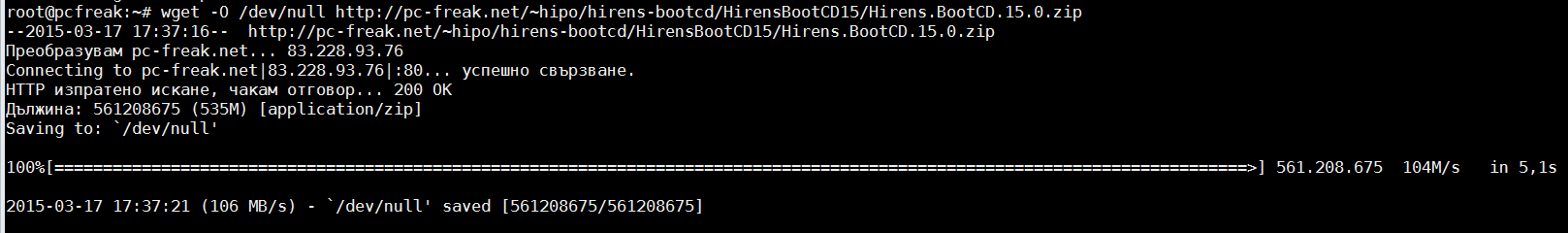
You see the Download speed is 104 Mbit/s this is so because I'm conducting the download from my local 100Mbit network.
For the test you can use my mirrored version of Hirens BootCD
2. Testing Uplink Internet speed provided by ISP / Server Provider from Linux (SSH) Console
To test your uplink speed you will need lftp or iperf command tool.
root@pcfreak:~# apt-cache show lftp|grep -i descr -A 12
Description: Sophisticated command-line FTP/HTTP client programs
Lftp is a file retrieving tool that supports FTP, HTTP, FISH, SFTP, HTTPS
and FTPS protocols under both IPv4 and IPv6. Lftp has an amazing set of
features, while preserving its interface as simple and easy as possible.
.
The main two advantages over other ftp clients are reliability and ability
to perform tasks in background. It will reconnect and reget the file being
transferred if the connection broke. You can start a transfer in background
and continue browsing on the ftp site. It does this all in one process. When
you have started background jobs and feel you are done, you can just exit
lftp and it automatically moves to nohup mode and completes the transfers.
It has also such nice features as reput and mirror. It can also download a
file as soon as possible by using several connections at the same time.
root@pcfreak:/root# apt-cache show iperf|grep -i desc -A 2
Description: Internet Protocol bandwidth measuring tool
Iperf is a modern alternative for measuring TCP and UDP bandwidth performance,
allowing the tuning of various parameters and characteristics.
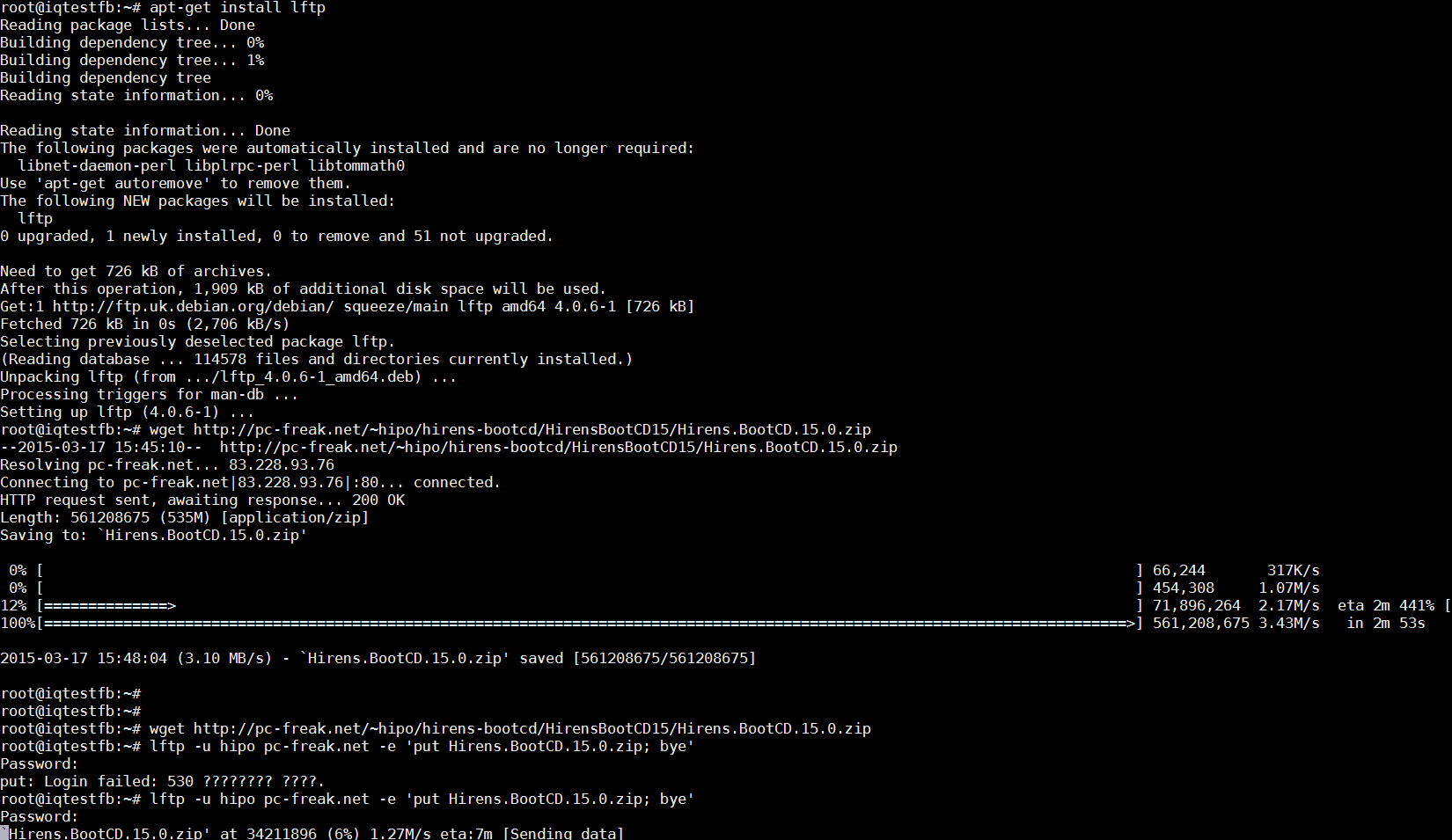
To test Upload Speed to Internet connect remotely and upload any FTP file:
root@pcfreak:/root# lftp -u hipo www.pc-freak.net -e 'put Hirens.BootCD.15.0.zip; bye'
On Debian Linux to install iperf:
root@pcfreak:/root# apt-get install –yes iperf
On latest CentOS 7 and Fedora (and other RPM based) Linux, you will need to add RPMForge repository and install with yum
[root@centos ~]# rpm -ivh rpmforge-release-0.5.3-1.el7.rf.x86_64.rpm
…
[root@centos ~]# yum -y install iperf
…
Once having iperf on the server the easiest way currently to test it is to use
serverius.net speedtest server – located at the Serverius datacenters, AS50673 and is running on a 10GE connection with 5GB cap.
root@pcfreak:/root# iperf -c speedtest.serverius.net -P 10
————————————————————
Client connecting to speedtest.serverius.net, TCP port 5001
TCP window size: 16.0 KByte (default)
————————————————————
[ 12] local 83.228.93.76 port 54258 connected with 178.21.16.76 port 5001
[ 7] local 83.228.93.76 port 54252 connected with 178.21.16.76 port 5001
[ 5] local 83.228.93.76 port 54253 connected with 178.21.16.76 port 5001
[ 9] local 83.228.93.76 port 54251 connected with 178.21.16.76 port 5001
[ 3] local 83.228.93.76 port 54249 connected with 178.21.16.76 port 5001
[ 4] local 83.228.93.76 port 54250 connected with 178.21.16.76 port 5001
[ 10] local 83.228.93.76 port 54254 connected with 178.21.16.76 port 5001
[ 11] local 83.228.93.76 port 54255 connected with 178.21.16.76 port 5001
[ 6] local 83.228.93.76 port 54256 connected with 178.21.16.76 port 5001
[ 8] local 83.228.93.76 port 54257 connected with 178.21.16.76 port 5001
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 9] 0.0-10.2 sec 4.05 MBytes 3.33 Mbits/sec
[ 10] 0.0-10.2 sec 3.39 MBytes 2.78 Mbits/sec
[ 11] 0.0-10.3 sec 3.75 MBytes 3.06 Mbits/sec
[ 4] 0.0-10.3 sec 3.43 MBytes 2.78 Mbits/sec
[ 12] 0.0-10.3 sec 3.92 MBytes 3.18 Mbits/sec
[ 3] 0.0-10.4 sec 4.45 MBytes 3.58 Mbits/sec
[ 5] 0.0-10.5 sec 4.06 MBytes 3.24 Mbits/sec
[ 6] 0.0-10.5 sec 4.30 MBytes 3.42 Mbits/sec
[ 8] 0.0-10.8 sec 3.92 MBytes 3.03 Mbits/sec
[ 7] 0.0-10.9 sec 4.03 MBytes 3.11 Mbits/sec
[SUM] 0.0-10.9 sec 39.3 MBytes 30.3 Mbits/sec
You see currently my home machine has an Uplink of 30.3 Mbit/s per second, that's pretty nice since I've ordered a 100Mbits from my ISP (Unguaranteed Bandwidth Connection Speed) and as you might know it is a standard practice for many Internet Proviers to give Uplink speed of 1/4 from the ISP provided overall bandwidth 1/4 would be 25Mbi/s, meaning my ISP (Bergon.NET) is doing pretty well providing me with even more than promised (ordered) bandwidth.
Iperf is probably the choice of most sysadmins who have to do regular bandwidth in local networks speed between 2 servers or test Internet Bandwidth speed on heterogenous network with Linux / BSDs / AIX / HP-UX (UNIXes). On HP-UX and AIX and other UNIXes for which iperf doesn't have port you have to compile it yourself.
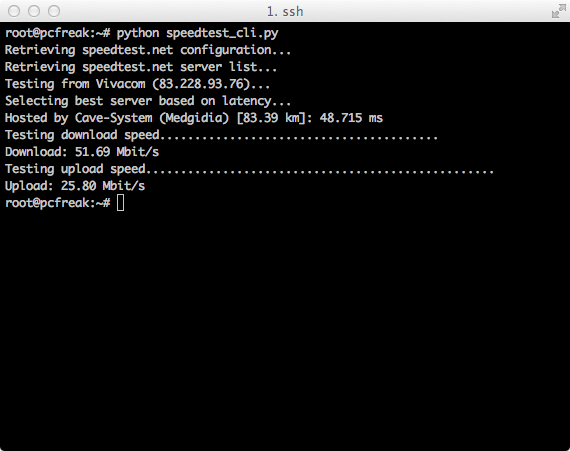
If you don't have root /admin permissions on server and there is python language enterpreter installed you can use speedtest_cli.py script to test internet throughput connectivity
speedtest_cli uses speedtest.net to test server up / down link just in case if script is lost in future I've made ownload mirror of speedtest_cli.py is here
Quickest way to test net speed with speedtest_cli.py:
$ lynx -dump https://raw.github.com/sivel/speedtest-cli/master/speedtest_cli.py > speedtest_cli.py
$ chmod +x speedtest_cli.py
python speedtest_cli.py






How to permanently enable Cookies in Lynx text browser – Disable accept cookies prompt in lynx console browser
Wednesday, April 18th, 2012The default behaviour of lynx – console text browser on Linuces, BSD and other free OSes is to always ask, for the accept cookies prompt once an internet web page is opened that requires browser cookies to be enabled.
I should admin, having this "secure by default" (always ask for new cookies) behaviour in lynx was a good practice from a security point of view.
Another reason, why this cookies prompt is enabled by default is back in the days, when lynx was actively developed by programmers the websites with cookies support was not that many and even cookies was mostly required for user/pass authentication (all those who still remember this days the websites that requires authentication was a way less than today) …
With this said the current continuing security cautious behaviour in the browser, left from its old days is understandable.
However I personally sometimes, need to use lynx more frequently and this behaviour of always opening a new website in text mode in console to prompts me for a cookie suddenly becomes a big waste of time if you use lynx to browser more than few sites. Hence I decided to change the default way lynx handles cookies and make them enabled by default instead.
Actually even in the past, when I was mainly using internet in console on every new server or home Linux install, I was again making the cookies to be permanently accepted.
Everyone who used lynx a few times already knows its "annoying" to all time accept cookie prompts … This provoked me to write this short article to explain how enabling of constant cookie accepting in lynx is done
To enable the persistent cookies in lynx, one needs to edit lynx.cfg on different GNU / Linux and BSD* distributions lynx.cfg is located in different directory.
Most of the lynx.cfg usual locations are /etc/lynx/lynx.cfg or /etc/lynx.cfg as of time of writting this post in Debian Squeeze GNU / Linux the lynx.cfg is located in /etc/lynx-cur/lynx.cfg, whether for FreeBSD / NetBSD / OpenBSD users the file is located in /usr/local/etc/lynx.cfg
What I did to allow all cookies is open lynx.cfg in vim edit and change the following lines:
a)
#FORCE_SSL_COOKIES_SECURE:FALSEwith
FORCE_SSL_COOKIES_SECURE:TRUEb)
#SET_COOKIES:TRUEuncomment it to:
SET_COOKIES:TRUEc) next, change
ACCEPT_ALL_COOKIES:FALSEACCEPT_ALL_COOKIES:TRUEOnwards opening any website with lynx auto-accepts the cookies.
For people who care about there security (who still browse in console (surely not many anymore)), permanently allowing the cookies is not a good idea. But for those who are ready to drop off little security for convenience its ok.
Tags: ALL, authentication, Auto, browser cookies, BSD, bsd distributions, cfg, change, convenience, Cookie, default behaviour, Draft, everyone, file, free oses, GNU, gnu linux, good, How to, internet web, Linux, Lynx, lynx one, NetBSD, Onwards, OpenBSD, page, persistent cookies, point of view, programmers, quot, reason, security point, squeeze, support, text, text browser, text mode, time, TRUEb, TRUEc, TRUEuncomment, uncomment, use, using internet, vim, waste, waste of time, web page, writ
Posted in Curious Facts, Everyday Life, FreeBSD, Linux, System Administration | 1 Comment »