Posts Tagged ‘httpd’
Wednesday, November 12th, 2014 
There are plenty of Apache Performance Optimization things to do on a new server. However many sysadmins miss .htaccess mod_rewrite rules whole optimization often leads to a dramatic performance benefits and low webserver responce time, making website much more attractive for both Search Engine Crawlers and End User experience.
Normally most Apache + PHP CMS systems, websites, blogs etc. are configured to use various goodies of .htaccess files (mostly mod_rewrite rules, directory htpasswd authentication and allow forbid directives). All most popular open-source Content management systems like Drupal, Joomla, WordPress, TYPO3, Symphony CMS are configured to get use .htaccess file usually living in the DocumentRoot of a virtualhost ( website/s ) – httpd.conf , apache2.conf /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/customvhost.com or whichever config the Vhost resides…
It is also not uncommon practice to enable .htaccess files to make programmers life easier (allowing the coder to add and remove URL rewrite rules that makes URL pretty and SEO friendly, handle website redirection or gives live to the framework like it is the case with Zend PHP Framework).
However though having the possibility to get the advantages of dynamically using .htaccess inside site DocRoot or site's subdirectories is great for developers it is not a very good idea to have the .htaccess turned on Production server environment.
Having
AllowOverride All
switched on for a directory in order to have .htaccess enabled, makes the webserver lookup for .htaccess file and re-read its content dynamically on each client request.
This has a negative influence on overall server performance and makes Apache preforked childs or workers (in case of mpm-worker engine used) to waste time parsing .htaccess file leading to slower request processing.
Normally a Virtualhost with enabled .htaccess looks like so:
<VirtualHost 192.168.0.5:80>
ServerName your-website.com:80 …
DocumentRoot /var/www/website
<Directory /var/www/website>
AllowOverride All …
</Directory> …
</VirtualHost>
And VirtualHost configured to keep permanently loaded mod_rewrite .htaccess rules in memory on Apache server start-up.
<VirtualHost 192.168.0.5:80>
ServerName your-website.com:80 …
DocumentRoot /var/www/website
<Directory /var/www/website>
AllowOverride None
Include /var/www/website/.htaccess …
</Directory> …
</VirtualHost>
Now CMS uses the previous .htaccess rules just as before, however to put more rewrite rules into the file you will need to restart webserver which is a downside of using rewrite rules through the Include directive. Using the Include directive instead of AllowOverride leads to 7 to 10% faster individual page loads.
I have to mention Include directive though faster has a security downside because .htaccess files loaded with Include option (uses mod_include) via httpd.conf doesn't recognize <Directory> … </Directory> set security rules. Also including .htaccess from configuration on Main Website directory, could make any other sub-directories .htaccess Deny / Allow access rules invalid and this could expose site to security risk. Another security downside is because Include variable allows loading a full subset of Apache directives (including) loading other Apache configuration files (for example you can even override Virtualsthost pre-set directives such as ErrorLog, ScriptAlias etc.) and not only .htaccess standard directives allowed by AllowOverride All. This gives a potential website attacker who gains write permissions over the included /var/www/website/.htaccess access to this full set of VirtualHost directives and not only .htaccess standard allowed.
Because of the increased security risk most people recommend not to use Include .htaccess rules, however for those who want to get the few percentage page load acceleration of using static Include from Apache config, just set your Included .htaccess file to be owned by user/group root, e.g.:
chown root:root /var/www/website/.htaccess
Tags: com, configured, downside, htaccess files, httpd, rewrite, security, server performance, VirtualHosts, webserver, www
Posted in Programming, System Administration, Various, Web and CMS | No Comments »
Tuesday, February 10th, 2015 
I've been recently writting this Apache webserver / Tomcat / JBoss / Java decomissioning bash script. Part of the script includes extraction from httpd.conf of DocumentRoot variable configured for Apache host.
I was using following one liner to grep and store DocumentRoot set directory into new variable:
documentroot=$(grep -i documentroot /usr/local/apache/conf/httpd.conf | awk '{ print $2 }' |sed -e 's#"##g');
Above line greps for documentroot prints 2nd column of the matchi (which is the Apache server set docroot and then removes any " chars).
However I faced the issue that parsed string contained in $documentroot variable there was mysteriously containing r – return carriage – this is usually Carriage Return (CR) sent by Mac OS and Apple computers. For those who don't know the End of Line of files in UNIX / Linux OS-es is LF – often abreviated as n – often translated as return new line), while Windows PCs use for EOF CR + LF – known as the infamous rn. I was running the script from the server which is running SuSE SLES 11 Linux, meaning the CR + LF end of file is standardly used, however it seem someone has editted the httpd.conf earlier with a text editor from Mac OS X (Terminal). Thus I needed a way to remove the r from CR character out of the variable, because otherwise I couldn't use it to properly exec tar to archive the documentroot set directory, cause the documentroot directory was showing unexistent.
Opening the httpd.conf in standard editor didn't show the r at the end of
"directory", e.g. I could see in the file when opened with vim
DocumentRoot "/usr/local/apache/htdocs/site/www"
However obviously the r character was there to visualize it I had to use cat command -v option (–show-nonprinting):
cat -v /usr/local/apache/conf/httpd.conf
…
DocumentRoot "/usr/local/apache/htdocs/site/wwwr"
…
1. Remove the r CR with bash
To solve that with bash, I had to use another quick bash parsing that scans through $directory and removes r, here is how:
documentroot=${documentroot%$'r'}
It is also possible to use same example to remove "broken" Windows rn Carriage Returns after file is migrated from Windows to Liunx / FreeBSD host:
documentroot=${documentroot%$'rn'}
2. Remove r Carriage Return character with sed
Other way to do remove (del) Windows / Mac OS Carriage Returns in case if Migrating to UNIX is with sed (stream editor).
sed -i s/r// filename >> filename_out.txt
3. Remove r CR character with tr
There is a third way also to do it with (tr) – translate or delete characters old shool *nix command:
tr -d 'r' < file_with_carriagereturns > file_without_carriage_returns
4. Remove r CRs with awk (pattern scanning and processing language)
awk 'sub("$", "r")' inputf_with_crs.txt > outputf_without_crs.txt
5. Delete r CR with VIM editor
:%s/r//g
6. Converting file DOS / UNIX OSes with dos2unix and unix2dos command line tools
For sysadmins who don't want to bother with writting code to convert CR when moving files between Windows and UNIX hosts there are dos2unix and unix2dos installable commands.
All done Cheers ! 🙂
Tags: apache, bash script, bash shell, conf, configured, Delete, directory, documentroot, file, hidden, httpd, vim, Windows
Posted in Curious Facts, Everyday Life, Programming, System Administration, Various | No Comments »
Wednesday, February 26th, 2014 
Having a combination of Apache webservice Reverse Proxy to redirect invisibly traffic to a number of Tomcat server positioned in a DMZ is a classic task in big companies Corporate world.
Hence if you work for company like IBM or HP sooner or later you will need to configure Apache Webserver cluster with few running Jakarta Tomcat Application servers behind. Scenario with necessity to access a java based application via Tomcat which requires logging (authentication) relaying on establishing and keeping a session ID is probably one of the most common ones and if you do it for first time you will probably end up with Session ID issues. Session ID issues are hard to capture at first as on first glimpse application will seem to be working but users will have to re-login all the time even though the programmers might have coded for a session to expiry in 30 minutes or so.
… I mean not having configured Session ID prevention to Tomcats will cause random authentication session expiries and users using the Tomcat app will be unable to normally access below application with authenticated credentials. The solution to these is known under term "Sticky sessions"
To configure Sticky sessions you need to already have configured Apache/s with following minimum configuration:
- enabled mod_proxy, proxy_balancer_module, proxy_http_module and or mod_proxy_ajp (in Apache config)
LoadModule proxy_module modules/mod_proxy.so
LoadModule proxy_balancer_module modules/mod_proxy_balancer.so
LoadModule proxy_http_module modules/mod_proxy_http.so
- And configured and tested Tomcats running an Application reachable via AJP protocol
Below example assumes there is Reverse Proxy Load Balancer Apache which has to forward all traffic to 2 tomcats. The config can easily be extended for as many as necessary by adding more BalancerMembers.
In Apache webserver (apache2.conf / httpd.conf) you need to have JSESSIONID configured. These JSESSIONID is going to be appended to each client request from Reverse Proxy to each of Tomcat servers with value opened once on authentication to first Tomcat node to each of the other ones.
<Proxy balancer://mycluster>
BalancerMember ajp://10.16.166.53:11010/ route=delivery1
BalancerMember ajp://10.16.166.66:11010/ route=delivery2
</Proxy>
ProxyRequests Off
ProxyPass / balancer://mycluster/ stickysession=JSESSIONID
ProxyPassReverse / balancer://mycluster/
The two variables route=delivery1 and route=delivery2 are routed to hosts identificators that also has to be present in Tomcat server configurations
In Tomcat App server First Node (server.xml)
<Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="localhost" jvmRoute="delivery1">
In Tomcat App server Second Node (server.xml)
<Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="localhost" jvmRoute="delivery2">
Once Sticky Sessions are configured it is useful to be able to track they work fine this is possible through logging each of established JESSSIONIDs, to do so add in httpd.conf
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"\"%{JSESSIONID}C\"" combined
After modifications restart Apache and Tomcat to load new configs. In Apache access.log the proof should be the proof that sessions are preserved via JSESSIONID, there should be logs like:
127.0.0.1 - - [18/Sep/2013:10:02:02 +0800] "POST /examples/servlets/servlet/RequestParamExample HTTP/1.1" 200 662 "http://localhost/examples/servlets/servlet/RequestParamExample" "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:17.0) Gecko/20130807 Firefox/17.0""B80557A1D9B48EC1D73CF8C7482B7D46.server2"
127.0.0.1 - - [18/Sep/2013:10:02:06 +0800] "GET /examples/servlets/servlet/RequestInfoExample HTTP/1.1" 200 693 "http://localhost/examples/servlets/" "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:17.0) Gecko/20130807 Firefox/17.0""B80557A1D9B48EC1D73CF8C7482B7D46.server2"
That should solve problems with mysterious session expiries 🙂
Tags: AJP, apache webserver, apache2, application, authentication, combination, conf, configured, DMZ, Engine, First Node, hp, httpd, ID, Jakarta Tomcat Application, JESSIONID, JSESSIONID, localhost, need, number, proof, proxy, request, Reverse Proxy, Reverse Proxy Load Balancer Apache, run, Second Node, server, session, working, xml
Posted in Linux, System Administration, Various | 2 Comments »
Friday, January 31st, 2014 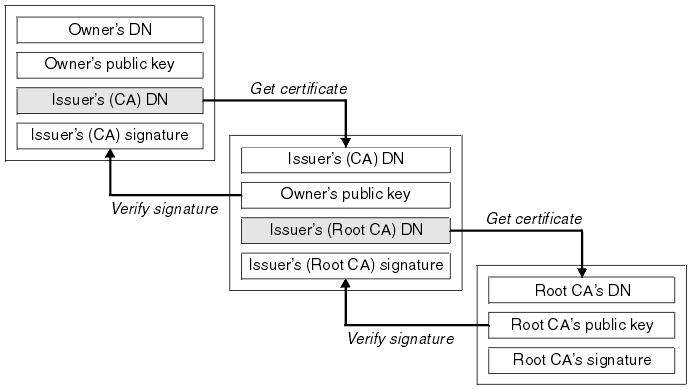
If you work in a big company with large network infrastructure who has to deal with SSL Certificates you will sooner or later will have to learn about existence of SSL Certificate Chains.
Its worthy thus to know what is SSL Certificate Chains and how such a chain is configured in Apache?
Personal SSL certificates (certificates issued to an individual or a company) can be used by clients to uniquely identify themselves when they are involved in starting an SSL connection.
SSL Certificate file contains X.509 certificate, which, in turn, contains a public key used for encryption.
Each personal certificate has zero or more certificate chains of certification authority certificates that extend back to the root certification authority.
Certificate R (Root Certification Authority)
|
| represents issuer of
V
Certificate I1 (Intermediate Certification Authority)
|
| represents issuer of
V
Certificate I2 (A subsidiary Intermediate Certification Authority)
|
| represents issuer of
V
Certificate I3 (A further subsidiary Intermediate Certification Authority)
|
| represents issuer of
V
Certificate P (A personal certificate that is used to identify its owner
on an SSL handshake)
Certificate chains are used to verify the authenticity of each certificate in that chain, including the personal certificate. Each certificate in the chain is validated using its 'parent' certificate, which in turn is validated using the next certificate up the chain, and so on, from the personal certificate up to the root certification authority certificate.
Now after explaining thoroughfully what is SSL Certificate Chain, here is how to configure a SSL Certificate in Apache Webserver.
Open apache2.conf or httpd.conf (depending on GNU / Linux distribution) and add to it;
SSLEngine On
SSLCertificateFile conf/cert/webserver-host.crt
SSLCertificateKeyFile conf/cert/webserver-host.key
SSLCertificateChainFile conf/cert/internet-v4.crt
# SSLCertificateChainFile conf/cert/intranet-v3.crt
SSLOptions +StdEnvVars +OptRenegotiate +ExportCertData
SSLCertificateChainFile conf/cert/chain-cert.crt
loads a chain of separate Personal SSL certificates each signing each other on different levels, chain is leading to top ROOT CA (Certificate Authority).
Tags: apache, apache2, cert, certificate, Certificate Chain, com, company, conf, configured, deal, existence, httpd, individual, installation, key, parent, root, signing, SSL, webserver, www
Posted in Linux, System Administration, Web and CMS | 1 Comment »
Saturday, March 31st, 2007 Yesterday the day was quite strained. We were prepairing for few weeks to host the new website of pozvanete.bgcreated by our firm Design.BG, so yesterday in 9:40, our project manager has called and said pozvanete.bg’s DNSrecord is already changed to point to our server, but there is a problem while http://www.pozvanete.bg opensnormally, http://pozvanete.bg opens DBG’s 404 error page. I remembered that this is due to a configuration of theserver cause there was some SEO stuff in the past on the server, so I was able to fix the problem quickly.The problems started to come after that. The machine where we hosted the site (and it was the only site there was1.6ghz AMD with 1 giga of RAM). Unfortunately 30 minutes after it started to open from our server I observed themachine’s cpu stays idle 0.0 all the time and the site responds very slowly to browser requests. I tried to tinkerit changing things from the webserver configuration file with no luck. I spoke with my boss explained him the situationso he decided we’ll move the site on another machine which is ( 3.0 Ghz Intel ), and the next week we’ll move the siteagain to a rack machine colocated in Sofia in Evo Link. It took a lot of conversations over the phone and talk with Vladibefore we moved completely the site on the new machine before that I have to recompile the machine’s current httpd and php to match the requirements of the site but Praise the Lord in the everything went smoothly and we were able to move the site completely the site to the new location. I’ve speak with Pozvanete’s administrator to change the DNS records to point to the new machine and in 6:00 o’clock the site could be seen from the new server. In the mean time Bobb has bought an IBM rack he quickly packed it and send it to Sofia. Among all this a lot of collegues from the office found me urgent work, I got a complaint about a problem with the mails of propertyinvestld the guy claimed our webmail sent the .doc files as winmail.dat which as I suspected was not true. But Praise the Lord everything went smoothly in the end. In 8:00 o’clock we go out of home with Nomen and decided to go to the Mino’s coffee to see Sami cause he’s has come back from Sofia. Mino’s coffee was a lot of fuller than usual, and it was very smoky, Tsetso speak a lot about art and history as usual, I was bored as usual etc. etc.After that we had the idea to watch a film in Nomen’s home but my Aunt called and said if I have time it will be good to see my grandma cause she is not feeling well (they made her eye surgery 3 days ago). I went to his home and stayed with her it’s awful she is such a nice lady and she’s suffering so much. She said how bad she felt nobody went to the hospital to see her for 3 days ( First I was angry to my mother .. then I calmed down ). I realized all the world is in birth pains as written in the Bible so I praid a lot to the Creator to have mercy over my grandma. Then I tried reading The Bible for some time but I was too sleepy and I went to bed. END—–
Tags: amd, Bobb, boss, browser requests, cause, clock, coffee, collegues, colocated, configuration file, conversations, CPU, dns records, everything, Evo, file, giga, grandma, httpd, intel, luck, manager, mean time, Mino, move, new location, page, phone, pozvanete bg, Praise, rack, RAM, siteagain, sofia, themachine, time, Vladibefore
Posted in Everyday Life | No Comments »
Saturday, October 15th, 2011 Since some time, I don’t know exactly where, after some updates of my WordPress running on a small server with FreeBSD 7.2. I’ve started getting a lot of Apache crashes. Often the wordpress scripts stopped working completely and I got only empty pages when trying to process the wordpress blog in a browser.
After a bunch of reading online, I’ve figured out that the cause might be PHP APC stands for Alternative PHP Cache .
I was not sure if the PHP running on the server had an APC configured at all so I used a phpinfo(); script to figure out if I had it loaded. I saw the APC among the loaded to show off in the list of loaded php modules, so this further led me to the idea the APC could be really causing the unexpected troubles.
Thus first I decided to disable the APC on a Virtualhost level for the domain where the crashing wordpress was hosted, to do I placed in the VirtualHost section in the Apache configuration /usr/local/etc/apache2/httpd.conf the following config directive:
php_flag apc.cache_by_default Off
These get me rid of the multiple errors:
PHP Warning: require_once() [function.require-once]: Unable to allocate memory for pool. in /usr/local/www/data-dist/blog/wp-content/plugins/tweet-old-post/top-admin.php on line 6
which constantly were re-occuring in php_error.log:
Further after evaluating all the websites hosted on the server and making sure none of which was really depending on APC , I’ve disabled the APC completely for PHP. To do so I issued:
echo 'apc.enabled = 0' >> /usr/local/etc/php.ini
Similarly on GNU/Linux to disable globally APC from PHP only the correct location to php.ini should be provided on Debian this is /etc/php5/apache2/php.ini .
Tags: apache, apache configuration, apc, blog, browser, cause, conf, config, configured, correct location, domain, error messages, freebsd, function, gnu linux, httpd, idea, ini, level, line, line 6, Linux, location, memory, OffThese, online, php cache, php error, pool, reading, scripts, time, virtualhost section, Warning, Wordpress, wordpress blog, www, www data
Posted in System Administration, Various, Wordpress | 1 Comment »
Sunday, September 25th, 2011 I’ve had two domain names which were pointing to the same website content.
As one can read in any SEO guide around this is a really bad practice as search engines things automatically there is a duplicate site content and this has automatically a negative effect on the site pagerank.
To deal with situation where multiple domains are pointing to the same websites its suggested by many SEO specialists that a 301 redirect is created from all the domain websites to a single website domain which will open the actual website.
Making the 301 direct domain from the sample domain my-redirect-domain.com to www.mydomain.com can be done with a virtualhost dfefinition in either httpd.conf or with the respective file containing the domain virtualhost definitions:
Here is the exact VirtualHost code I use to make a 301 redirect.
<VirtualHost *>
ServerAdmin support@mydomain.com ServerName my-redirected-domain.com
ServerAlias my-redirected-domain.com www.my-redirected-domain.com
RewriteEngine on RewriteRule ^/(.*) http://www.mydomain.com/$1 [L,R=301]
</VirtualHost>
After placing the VirtualHost redirect, an apache redirect is required.
Further on when a Gooogle or Yahoo Bot visits the website and does any request to my-redirect-domain.com or www.my-redirect-domain.com , they will be redirected with a 301 reuturned code to www.mydomain.com
This kind of redirect however can have a negative impact on the Apache CPU use (performance), especially if the my-redirect-domain.com is high traffic domain. This is because the redirect is done with mod_rewrite.
Therefore it might be better on high traffic domains to create the mod_rewrite redirect by using a vhost like:
<VirtualHost *>
ServerAdmin support@mydomain.com
ServerName my-redirected-domain.com
Redirect 301 / http://www.mydomain.com/
</VirtualHost>
The downside of using the Apache 301 redirect capabilities like in the above example is that any passed domain urls like let’s say http://www.my-redirected-domain.com/support/ would not be 301 redirected to http://www.mydomain.com/support/ but instead the redirect will be done straight to http://www.mydomain.com/
Tags: apache, capabilities, com, conf, CPU, definitions, domain names, domain websites, downside, Gooogle, guide, httpd, impact, kind, lt, mydomain, nbsp, negative impact, pagerank, rewrite, RewriteEngine, RewriteRule, Search, search engines, seo specialists, ServerName, traffic domain, traffic domains, use, vhost, Virtualhost, website content, website domain, www, Yahoo
Posted in SEO, System Administration, Various, Web and CMS | 2 Comments »








