Everything actually started in Friday. Friday I was on a Webtech in Varna in the Technical University.This is the second Webtech conference made in Varna. I was on the lectures until dinner. Firstwe went with Nomen, Niki and Dancho to the TU University, and we lost some time searching for theroom after that we found the room where the lectures were going to be. We entered in the endingpart of the first introductionary lecture about webtech. After this there was a lecture forperl Catalyst, which was quite interesting btw after that a lecture for expect (hackman has leaded the lecture).After that we went to drink a coffee and I found out I have lost my wallet. I get mad because I thoughtwell God I try to be good to others to give to the poor etc. etc. and in return I loose 42 lv. I spendthe other part of the day staying alone on a bench outside the university and thinking about the humanexistence, after that I went home very disappointed and angry. Stelio a friend who is has led me to the Orthodox Christianianity. Called and I invited him to be my guest, we had a great time togetherdiscussing the human existence. The next day I wake up early and I was feeling awful, meaninglesslost. Nomen called and said there are on the 2nd day on the lectures of webtech conference againand that my wallet has been found with 42 lv. and my ID card in it. I PRAISED THE LORD! It wasquite a joyful for me. On the next day I decided I would go to the Manowar concert in Kavarnaand I bought the ticket from Amridikon. The concert was interesting as a whole but I realizedI’m not into metal music anymore. After that Nomen came and take me from Kavarna with a car andwe went to Tulenovo’s rocks awaiting the July Morning with some other friends (Sami, Toto, Iasho, Gegi etc.).The rocks were very beautiful and the sea’s view is great. We baked some meet and ate. In the morning, there was a Metal July. (Toto, Sami and Iasho banged there heads on Sepultura’s Roots Bloody Rootsand Territory. After that we made a sort of excursion in the Village of Tulenovo and around it around the rocks.We then moved to Balchik to leave one of the girls with us on the station to take a bus for her working place.And in the end we come back to Dobrich in 10. I was tired as hell. And sleep until 3. I then attended the Orthodox Church st. Georgi to pray to God. Later I bought some vegetables and fruits fromthe open market for my Grandma. And went to her home to give her the products. After that I saw lily on a coffee.And in the late afternood we had a walk with Nomen into the central park. Nomen suggested that it would be cool to drink beer in hishouse and to watch the film (Die Young 3) and that’s exactly what we did. This few days was quite a colorful It’s God behind thisstarting to answer my prayers slowly but surely. Thanks God for giving me all thiswonderful moments :]END—–
Posts Tagged ‘card’
Manowar in Kavarna
Monday, July 2nd, 2007Tags: andwe, bench, btw, card, Catalyst, Christianianity, coffee, concert, Dancho, everything, existence, forperl, god, great time, hackman, human existence, Kavarnaand, lecture, lv, Metal, metal music, morning, niki, rocks, roots, sepultura, Stelio, Technical, theroom, ticket, time, Tulenovo, University, varna, wallet, wasquite, webtech
Posted in Everyday Life | No Comments »
End of Management Games / Lectures
Wednesday, April 16th, 2008Today was the last day of the lectures with Joop Vinke. Here is how my day passed. I woke up at 9:00, washed my teeth dressed combed my hair and went to the police station to look for our quarter police officer. I need to renew my personal ID card because it has been expired already for 4 years already. Thanks God everything went smoothly in the police station. After that I went to school we had lectures with Joop Vinke. After the school I went home and played around with my FreeBSD system. I succesfully upgraded gnome 2.20 to 2.22.
Using the binary packages from
http://www.marcuscom.com/tb/packages/7-STABLE-FreeBSD/gnome/. I’m trying to upgrade gnome from source for already almost 3 weeks with portmanager. After all of the required ports rebuilded still gnome wasn’t functioning, so in order to make it working I downloaded packages from http://www.marcuscom.com/tb/packages/7-STABLE-FreeBSD/gnome/ and ran a little loop with
for i in *; do pkg_add -vf $i; done
to make all the .tbz files install I did that yesterday night today at the afternoon everything was installed and gnome ran just fine I only had to link few libraries because they were searched on a different places. All works just fine now I only have to rebuild few of my games because they’re now linked to an old libraries. In the evening we went out with Javor for a coffee. As very often we went to the fountain we had a nice talk and then we went to his apartment to watch a film. He recommended a film called 1984 and we watched that. My impression is that this film is totally psychodelic and freaky, but still interesting to see. After I went home I went to see my grandma and now I’m home tired on a few steps of my bed 🙂 I should also mention that today I upgraded clamav on 3 of the servers I maintain. It seems there are few configuration options which changed in the new clamav release (0.93). It was an easy day as a whole if we don’t count my physical infirmity.
END—–
Tags: bed, binary packages, card, Clamav, coffee, configuration options, count, different places, end, everything, freaky, freebsd system, functioning, Gnome, grandma, impression, infirmity, Javor, Joop, Lectures, libraries, management games, nbsp, night today, personal id card, physical infirmity, pkg, police, police officer, police station, ports, station, tb, tbz, teeth, vf, yesterday
Posted in Entertainment, Gnome | No Comments »
How to fix “Out of Range” resolution problems with NVIDIA Riva TNT2 Model 64/Model 64Pro with BENQ FP61E
Friday, January 20th, 2012Today I had a task to change an old CRT Monitor to LCD BENQ Model FP61E on a computer running Microsoft Windows XP SP3.
Changing phyiscally the monitors and restarting the computer to load with the new BENQ monitor ended up with the LCD Monitor showing a blank screen with error:
Out of Range
making the computer completely unusable.
Thanksfully in Windows Safe Mode the monitor was able to display the screen properly, so I had an option to operate somehow on the pc
My guess was that the Out of Range monitor problems were caused by an incorrect (monitor unsupported resolution).
Therefore what I tried as a fix to make it work was:
1. Enter Windows Safe Mode and change (lower the resolution) to 640×480, and restart the PC.
Unfortunately using this classical way to fix such issues failed… so I thought of some options.
2. Disable the video card NVIDIA Riva TNT2 Model 64 driver and check if this will make any difference.
I come up with the idea the Out of Range LCD issues might be caused by the Video card driver cause I've noticed in safe mode a standard VESA like VGA Driver shipped with Windows worked just fine.
To Disable the currently loaded NVIDIA Riva TNT2 Model 64/ Model 64Pro I used:
System -> Device Manager -> Hardware (Tab) -> Display Adapters
Clicking on Display Adapters the NVIDIA Riva TNT2 Model 64 appears using the option menu on it one can choose to disable the driver.
Further on restart Windows, to test if the XP will load properly with disabled NVidia video drivers.
Onwards it was clear the whole Out of Range issues were caused by some kind of conflict between the LCD BENQ FP61E Monitor and the NVIDIA Riva TNT2 Model 64
Often latest video drivers solves hardware incompitability issues and fix many bugs, upgrading the driver to latest is always a good idea.
3. Therefore I Upgraded the NVIDIA Riva TNT2 64 driver (using Safe Mode) to the latest available from Nvidia's official site.
Weirdly Upgrading NVidia Riva TNT2 drivers to the latest did not fix the Out of Range blank screen error.
After a bit of thinking on what to do to make the Monitor work fine with the Nvidia driver, I thought of completely uninstalling the Nvidia drivers and installing them again might be a fix.
In my previous experience with Windows at many occasions, uninstalling a driver failing to properly work and installing it again with a working version was a good fix.
4. Uninstall the NVIDIA Riva TNT2 Model and Install the latest driver.
Uninstalling and Installing the Video driver had to be done in Windows Safe Mode again, in normal mode the windows was not displaying anything.
After The driver installation program completes the installation it requires a restart. After the restart the Video driver gets loaded fine and Windows loaded up in Normal mode as usual 😉
Tags: Auto, blank screen, card, cause, change, CRT, device manager, Display, display adapters, Draft, hardware tab, Install, installation, manager gt, menu, microsoft windows, Model, monitor problems, nvidia, nvidia riva tnt2 64, nvidia riva tnt2 64 driver, nvidia riva tnt2 model 64, nvidia video drivers, Onwards, option, option menu, range resolution, resolution problems, riva tnt2 model 64, Safe, screen, tnt2 model 64 driver, Uninstalling, Upgraded, vesa, VGA, vga driver, video card driver, Weirdly, windows safe mode, work
Posted in Everyday Life, Windows | No Comments »
How to solve ALSA sound problems with old Linux programs and games depending on (OSS)’s /dev/dsp / fix wine games and pulseaudio problems – My few thoughts on OSS and ALSA
Wednesday, January 11th, 2012
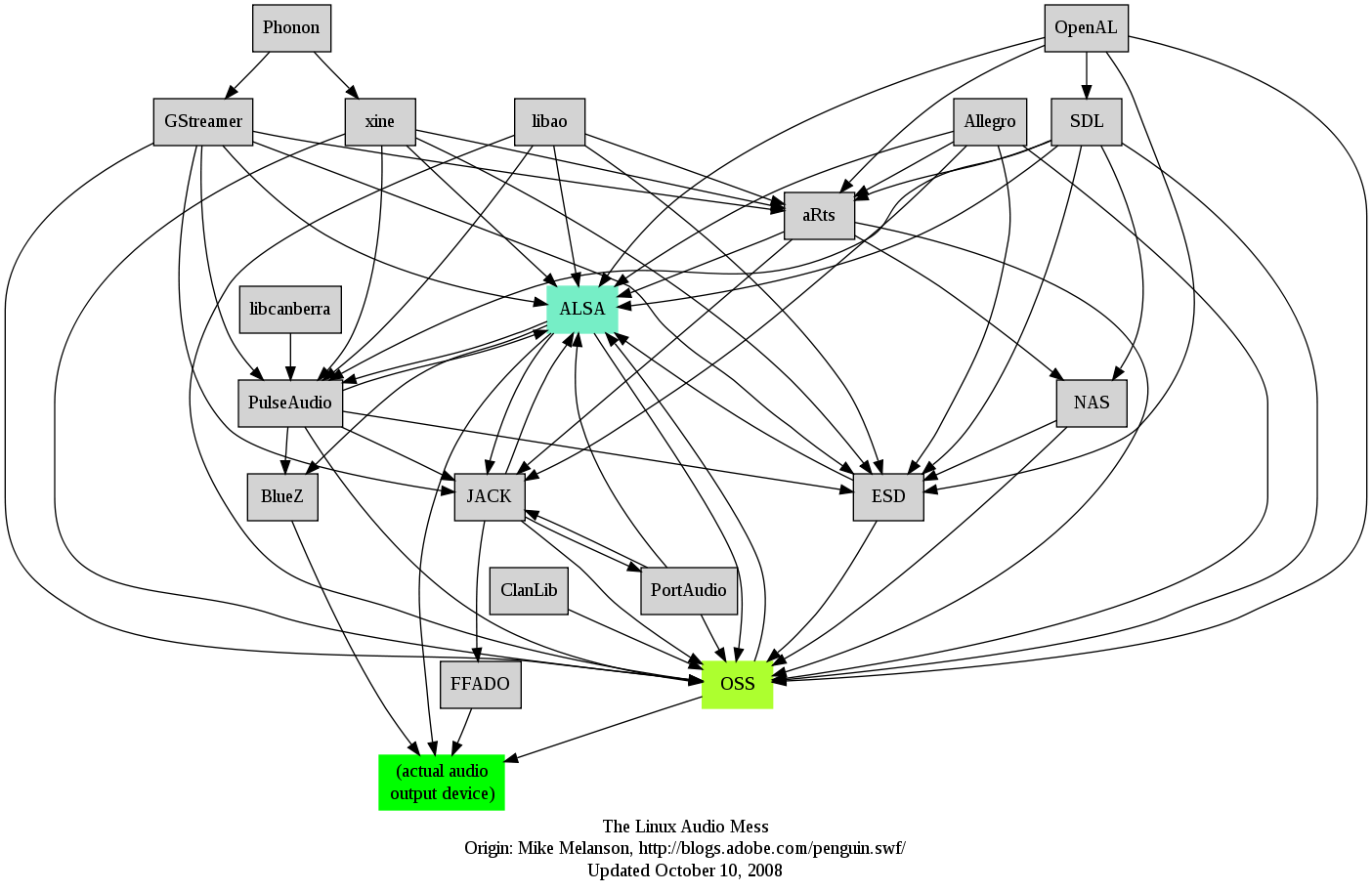 I remember GNU / Linux, 11 years from now, times when ALSA was not standardly shipped with Linux.
I remember GNU / Linux, 11 years from now, times when ALSA was not standardly shipped with Linux.
Back then ALSA still lacked good support for many SoundCards and was still a "baby project".
In that time what we used to have sound on Linux was OSS – Open Sound System. OSS emerged right after the first ever Linux sound system VoxWare (formerly known as the Linux Sound Driver).
Back in those days OSS was used for multimedia support on both GNU / Linux and BSD based free OSes. It was few years later when I heard and used ALSA for a fist time and it wasn't really a love from first sigth.
One can easily find out by the name ALSA it is a system especially built for the Linux kernel and that's one of the reasosn why *BSD systems has their custom separate sound system.
There is plenty of reasons why OSS was substituted with ALSA. Main reason was its commercial like license, OSS wasn't completely "open source" GPLed (free software), there was resctions on use of OSS for commercial goals.
With its emerge ALSA started to push away OSS slowly. Somewhere in 2003, alsa has officially entered the Linux kernel source and until 2005 it was the default standard for all GNU / Linux operating systems.
As of time of writting ALSA has become the only sound system to have support for multiple sound card devices for Linux.
My experiences with ALSA, however ain't so nice if I take a look in my past experiences.
Since the very beginning of using ALSA, I had plenty of troubles with configuring properly my sound card not to mention, even after configuring it the MIDI support was not there.
Besides all the troubles main problems were stemming from the many applications still written to use OSS as sound system and hence with those sound was impossible with ALSA.The most problematic thing about apps written with OSS in mind was all of them tried to stream sound via /dev/dsp (OSS Digital Sound Processor), since alsa did not used /dev/dsp those programs was soundless.
On the other hand OSS was creating issues as well, one severe problem with OSS was the inability to stream multiple sounds simultaneously, because each sound stream required to pass voice through /dev/dsp and usually there was only one /dev/dsp.
The message;
/dev/dsp: Device or resource busy
and the proceeding irritation that used to annoy us in the early GNU / Linux days had of course some raw workarounds hacks but generally the workaround did not fix problems always.
Introduction of alsa free us from /dev/dsp issues but on the other handy has created a whole ocean of new BIG problems …
ALSA has modular structure and this imposes a great problem nowdays. The modular architecture is generally a good idea, however the way this was implemented within ALSA is far away from clear and easy to understand by the end user and therefore makes it very unintuitive and obscure.
Alsa misses simplicity which somehow was partially in the days of OSS. Thinking over the general situation with Linux multimedia nowdays, I believe it was exactly ALSA Project responsible for the so delayed mass Desktop Linux adoption.
Many long year standing Linux users had certainly had the alsa troubles during new system installs (correct me if I'm wrong).
The only fix to multiple soundcard initialization problems was to download alsa source and compile from source and hence made it hard and discouraging for people giving Linux a try.
This kind of ALSA "brokenness" pattern continues even to this very day (in Debian) Linux and probably building the alsa system from source is among the good practices to have a functional Linux sound system…
With all said the historic reason why ALSA was not quickly adopted and still is not a preferred default system for many applications ported to Free Software OSes by commercial company vendors is clear. Its simply not working out of the box …
Hope some ALSA developers will read this post work on changing the crazy structure of ALSA over complexity. ALSA needs automate way to solve issues with itself, the configuration should be more trivial and unified if Linux has to become more attractive for Desktop adoption.
Anyways, after the few words of history and indicating my pesonal observations on ALSA. I will proceed and explain few things on how ALSA can be configured to support and play nice with OSS dependant programs as well some basic explanations on common incompatibility between esd and pulseaudio and how this can be fixed;.
To assure nowdays OSS API built programs and games would work with Alsa its necessery to have installed;
ALSA wrapper for OSS applications
On Debian, Ubuntu, Fedora and most Linux distributions the Alsa OSS compatability layer comes under a (deb / rpm) package named alsa-oss
To install OSS compatability on Debian, Ubuntu and the like Debian based distributions issue:
debian:~# apt-get install alsa-oss alsaplayer-oss
...
On Fedora and other rpm based distributions install is with:
[root@fedora ~]# yum install alsa-oss alsaplayer-oss
...
alsa-oss provides with a command called aoss that should be used to work around some issues with old applications still depending on OSS:
hipo@debian:~$ aoss programName
Using aoss is helpful especially in situations if you have to run programs which deal with MIDI and others which somehow want to use /dev/dsp
There is also alternative way to enable alsa native support for MIDI and OSS by loading 3 kernel modules:
debian:~# modprobe snd-seq-oss
debian:~# modprobe snd-pcm-oss
debian:~# modprobe snd-mixer-oss
Note! The three modules has to be separately build using kernel source at most cases and does not come with most Linux distributions, so on many installations (including my current), they will be missing. If for you they load properly or you have customly build them add them also to load on system boot, like so:
echo 'snd-seq-oss' >> /etc/modules
echo 'snd-pcm-oss' >> /etc/modules
echo 'snd-mixer-oss' >> /etc/modules
The Linux sound situation becomes even more messy when ESD enters the scene. Many of the novice new Linux users certainly don't remember (Enlightened Sound Daemon) . ESD historically preceded PulseAudio . Hence it will be good to mention ESD was used for few years in GNOME and in around 2006-2007 it was substituted by PulseAudio.
Many applications, however who was ported or written for Linux especially (the proprietary ported ones) was already built to work with ESD and even though newer GNOME releases was fully using pulseaudio, this (non free software apps and games) were still depending on ESD.
The situation was partially fixed by creation of module for pulseaudio which added emulation support for esd . This was done by a module library for pulseaudio called libprotocol-esound.so
The package for almost all Linux distributions which does the esd emulation via pulse is pulseaudio-esound-compat . In latest Fedora Linux pulseaudio-esound-compat is installed by default.
In Debian and other Linux distributions it might need to be installed via apt with;
debian:~# apt-get install pulseaudio-esound-compat
...
pulseaudio-esound-compat solves some of the ESD app incompability but not always …
Handy tool also worthy to mention in solving PulseAudio, OSS incompatibility issues is padsp
padsp is helpful in solving obsolete issues with OSS applications (trying to access /dev/dsp) and therefore unable to communicate with Pulseaudio
padsp – is a PulseAudio OSS Wrapper.
An example where padsp is helpful is in case of /dev/dsp errors like:
/dev/dsp: Device or resource busy
Could not open /dev/dsp
Another common problem with sound on Linux is when running windows applications (running windows games with wine).
Quite often sound fails to work since wine tries to directly communicate with alsa and fails because alsa sound channel is taken by pulseaudio.
To workaround wine issues with pulseaudio, one of the solutions is to temporary stop pulseaudio, before running the wine emulated application:
hipo@debian:~$ pulseaudio --kill
Later on when the windows wine emulation is completed, pulseaudio has to be started once again in order to make Pulseaudio applications produce sound again, e.g. one has to issue:
hipo@debian:~$ pulseaudio --start
Alternative way to workaround wine sound issues is by using a script to kill pulseaudio every second. Here is fix_pulseaudio_wine_sound_probs.sh script
This script was reported by many people as fix to problems with wine games failing to play sounds and music, anyhow I personally prefer using the stop / start pulseaudio method.
The picture below is taken from Wikipedia and illustrates, clearly the intergalactical complexity of sound systems on Gnu / Linux and BSD
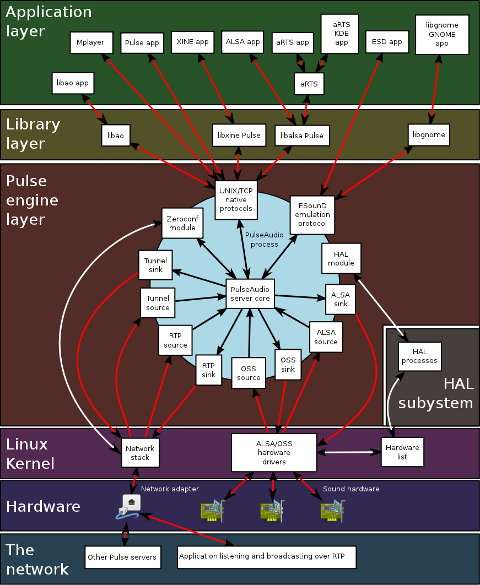
I just hope one day this (OSS, ALSA, esd, Pulseaudio) mess will be over! In the mean time I hope my suggested work arounds helps someone. If someone has a better more unified script or solution please share in comments
Tags: alsa, apps, baby project, BSD, bsd systems, card, commercial goals, custom, Desktop, Driver, dsp, experiences, fist time, free oses, GNU, GPLed, Linux, linux kernel source, linux programs, love, midi support, multimedia support, nbsp, Open, open source, operating systems, pulseaudio, quot, reason, right, software, sound card, soundcards, structure, support, time, Ubuntu, wine, wine games
Posted in Linux, Linux and FreeBSD Desktop, Linux Audio & Video | 3 Comments »
Solve ALSA audio and mic issues on Lenovo Thinkpads on Debian and Ubuntu Linux
Wednesday, January 11th, 2012Since I've blogged about my recent skype issues. I've played a lot with pulseaudio, alsa, alsa-oss to experimented a lot until I figured out why Skype was failing to properly delivery sound and record via my embedded laptop mic.
Anyways, while researching on the cause of my Thinkpad r61 mic issues, I've red a bunch of blog posts by people experiencing microphone oddities with Lenovo Thinkpads
Throughout the search I come across one very good article, which explained that in many cases the Thinkpad sound problems are caused by the snd-hda-intel alsa kernel module. snd-hda-intel fails to automatically set proper sb model type argument during Linux install when the soundcard is initialized with some argument like options snd-hda-intel model=auto
Hence, the suggested fix which should resolve this on many Thinkpad notebooks is up to passing the right module argument:
To fix its neceessery to edit /etc/modprobe.d/alsa-base.conf .
debian:~# vim /etc/modprobe.d/alsa-base.conf
Find the line in the file starting with:
options snd-hda-intel model=
and substitute with:
options snd-hda-intel model=thinkpad
Finally a restart of Advaned Linux Sound Architecture (alsa) is required:
debian:~# /etc/init.d/alsa restart
...
At most cases just restarting the alsa via its init script is not enough, since the ssnd-hda-intel kernel module is already in use by some program or something, so its best to do a reboot to make sure the module is loaded with the new model=thinkpad argument.
My exact laptop sound card model is:
debian:~# lspci |grep -i audio
00:1b.0 Audio device: Intel Corporation 82801H (ICH8 Family) HD Audio Controller (rev 03)
After changing the module and using alsamixer and aumix to make sure mic is unmuted and its volume is high enough, mic sound rec works fine.
Tags: Advaned, alsa, alsamixer, architecture, argument, audio controller, aumix, Auto, blogged, card, card model, cause, confFind, Draft, file, init, init script, intel corporation, kernel module, laptop, microphone, model auto, model type, modprobe, new model, oddities, pulseaudio, Reboot, script, Search, snd, Solve, something, sound architecture, sound card, soundcard, ssnd, substitute, thinkpad notebooks, thinkpad r61, thinkpads, type, type argument, Ubuntu, vim
Posted in Linux, Various | No Comments »
Upgrading Skype 2.0 to Skype 2.2 beta on Debian GNU / Linux – Skype Mic hell
Saturday, December 31st, 2011
Though, I'm GNU / Linux user for many years now. I have to say, everything is not so perfect as many people present it.
Configuring even simple things related to multimedia on Linux is often a complete nightmare.
An example, today I've decided to upgrade my 32 bit Skype version 2.0 beta for Linux to 64 bit Skype 2.2 beta .
The reason I was motivated to upgrade skype was basicly 2.
a) My Skype run through 32 bit binary emulation with /usr/bin/linux32
b) I had issues with my skype if someone give me a Skype Call, while I have a flash video or some other stream in Browser (let's say Youtube).
Actually being unable to receive a skype call or initiate one while I have some kind of music running in the background or just some kind of Youtube video paused was really annoying. Hence until now, everytime I wanted to speak over skype I had to close all Browser windows or tabs that are using my sound card and then restart my Skype program ….
Just imagine how ridiculous is that especially for a modern Multimedia supporting OS as Linux is. Of course the problems, I've experienced wasn't directly a problem of Linux. The problems are caused by the fact I have to use the not well working proprietary software version of Skype on my Debian GNU / Linux.
I would love to actually boycott Skype as RMS recommends, but unfortunately until now I can't, since many of my friends as well as employers use Skype to connect with me on daily basis.
So in a way I had to migrate to newer version of skype in order to make my Linux experience a bit more desktop like …
Back to the my skype 2.0 to 2.2. beta upgrade story, the overall Skype upgrade procedure was easy and went smootlhy, setting correct capturing later on however was a crazy task ….
Here is the step by step to follow to make my upgraded skype and internal notebook mic play nice together:
1. Download 64 bit Skype for Debian from skype.com
For the sake of preservation in case it disappears in future, I've made a mirror of skype for debian you can download here
My upgrade example below uses directly the 64 bit Skype 2.2beta binary mirror:
Here are the cmds once can issue if he has to upgrade to 2.2beta straight using my mirrored skype:
debian:~# wget https://www.pc-freak.net/files/skype-debian_2.2.0.35-1_amd64.deb
...
2. Remove the old version of skype
In my case I have made my previous skype installation using .tar.bz2 archive and not a debian package, however for some testing I also had a version of skype 2.0beta installed as a deb so for the sake of clarity I removed the existing skype deb install:
debian:~# dpkg -r skype
...
3. Install skype-debian_2.2.0.35-1_amd64.deb downloaded deb
debian:~# dpkg -i skype-debian_2.2.0.35-1_amd64.deb
...
After installing skype, I installed pavucontrol – A volume control for the PulseAudio sound server
4. Install pavucontrol
debian:~# apt-get install pavucontrol
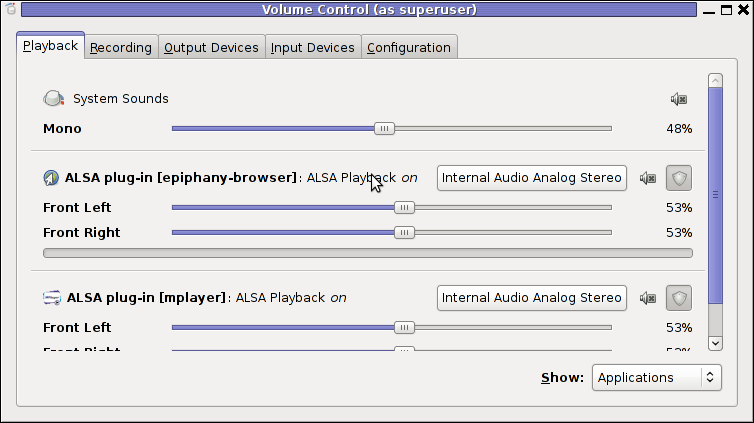
Pavucontrol has plenty of sound configurations and enables the user to change many additional settings which cannot be tuned in alsamixer
pavucontrol was necessery to play with until I managed to make my microphone able to record.
5. Build and install latest Debian (Testing) distribution alsa driver
debian:~# aptitude install module-assistant
debian:~# m-a prepare
debian:~# aptitude -t testing install alsa-source
debian:~# m-a build alsa
debian:~# m-a install alsa
debian:~# rmmod snd_hda_intel snd_pcm snd_timer snd soundcore snd_page_alloc
debian:~# modprobe snd_hda_intel
debian:~# echo 'options snd-hda-intel model=auto' >> /etc/modprobe.d/alsa-base.conf
In my case removing the sound drivers and loading them once again did not worked, so I had to reboot my system before the new compiled alsa sound modules gets loaded …
The last line echo 'options snd-hda-intel model=auto' … was necessery for my Thinkpard r61 Intel audio to work out. For some clarity my exact sb model is:
debian:~$ lspci |grep -i audio
00:1b.0 Audio device: Intel Corporation 82801H (ICH8 Family) HD Audio Controller (rev 03)
For other notebooks with different sound drivers echo 'options snd-hda-intel model=auto' … should be omitted.
6. Tune microphone and sound settings in alsamixer
debian:~$ alsamixer
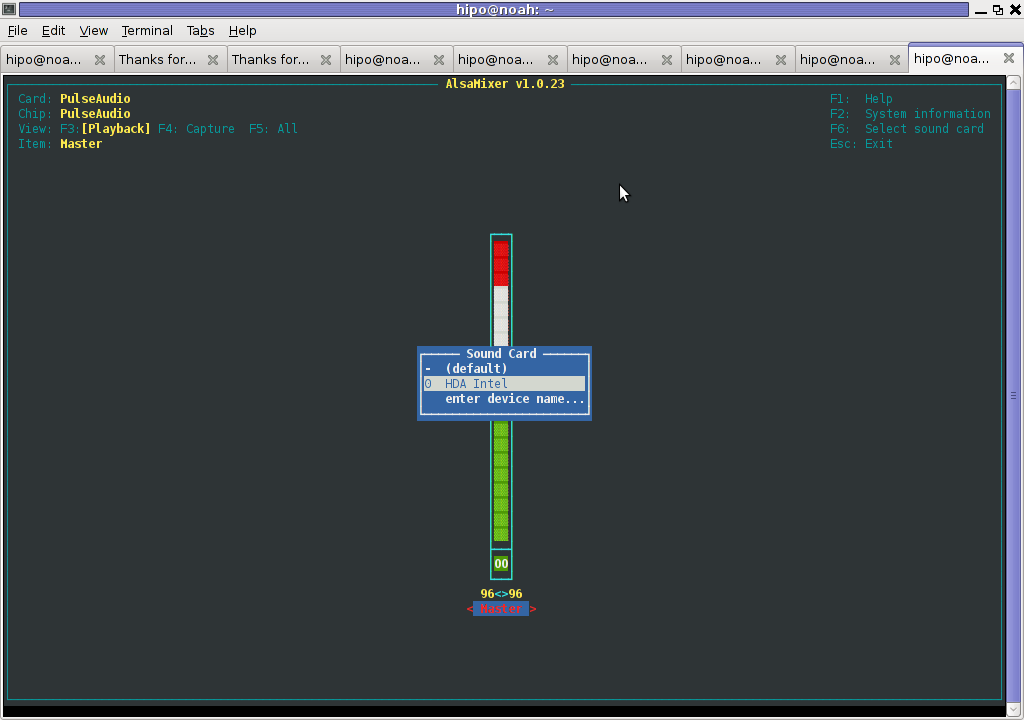
Right after launching alsamixer I had to press F6: Select Sound Card and choose my sound card (0 HDA Intel).
Following my choice I unmuted all the microphones and enabled Microphone Boost as well as did some adjustments to the MIC volume level.
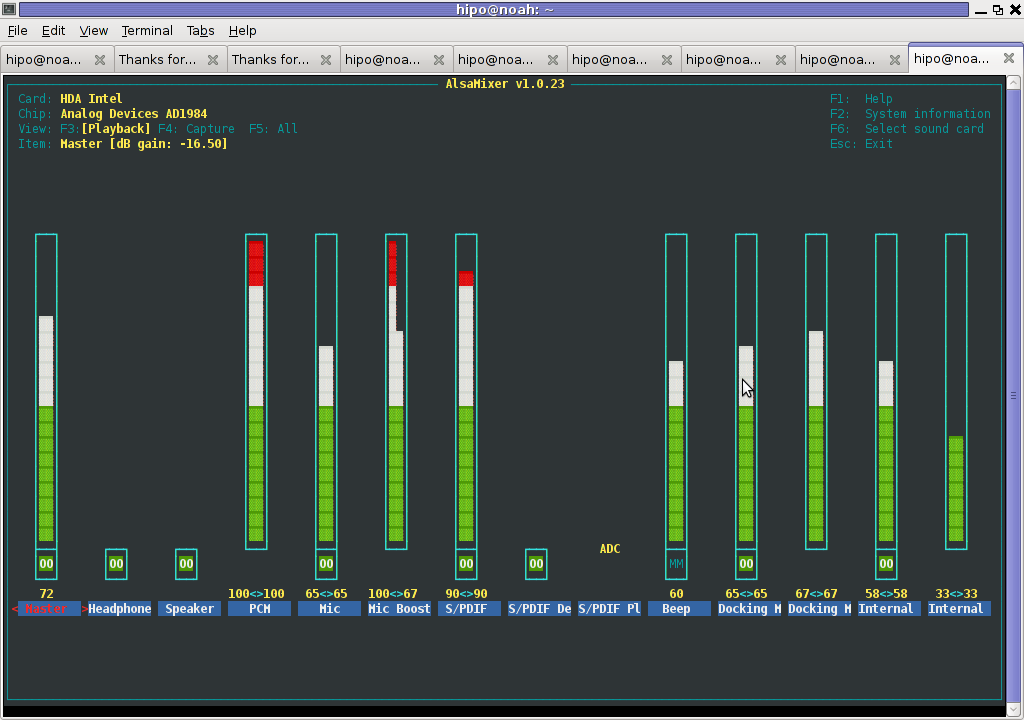
Setting proper MIC Volume levels is absolutely necessery, otherwise there is a constant noise getting out of the speakers …
7. Use aumix to set some other sound settings
For some unclear reasons, besides alsamixer , I often had to fix stuff in aumix . Honestly I don't understand where exactly aumix fits in the picture with Alsa and my loaded alsa sound blaster module?? If someone can explain I'll be thankful.
Launch aumix to further adjust some sound settings …
debian:~$ aumix
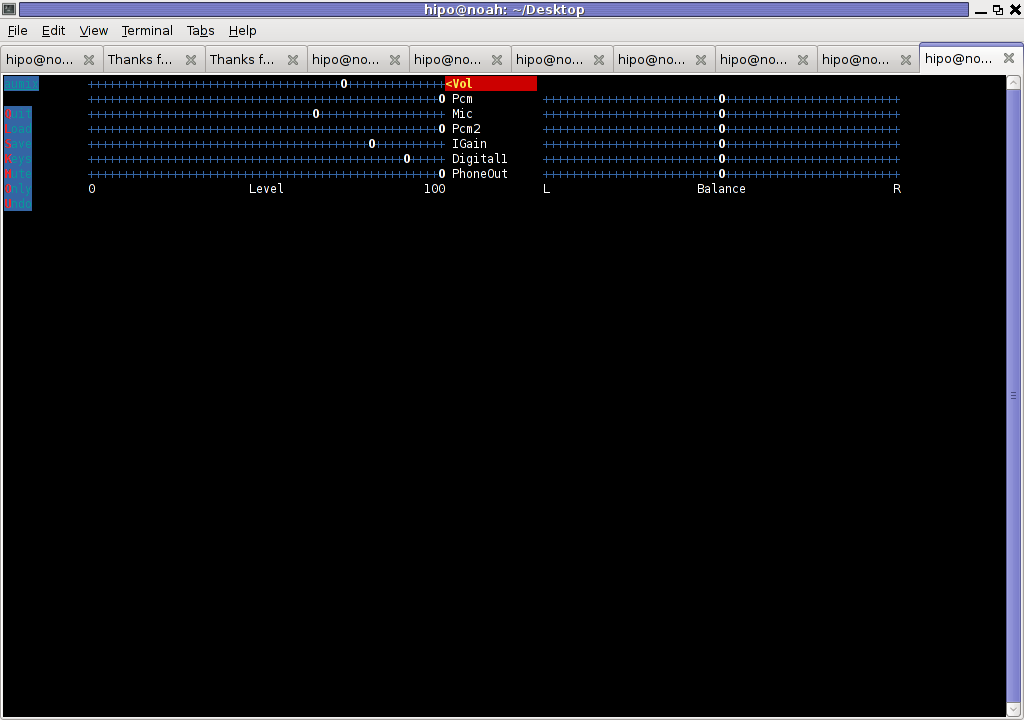
In above screenshot you see, my current aumix settings which works okay with mic and audio output.
9. Test Microphone the mic is capturing sounds correctly
Set ~/.asoundrc configuration for Skype
Edit ~/.asoundrc and put in:
pcm.pulse {
I'm not 100% percent if putting those .asoundrc configurations are necessery. I've seen them on archlinux's wiki as a perscribed fix to multiple issues with Skype sound in / out.
type pulse
}
ctl.pulse {
type pulse
}
pcm.!default {
type pulse
}
ctl.!default {
type pulse
}
pcm.card0 {
type hw
card 0
}
ctl.card0 {
type hw
card 0
}
pcm.dsp0 { type plug slave.pcm "hw:0,0" }
pcm.dmixout {
# Just pass this on to the system dmix
type plug
slave {
pcm "dmix"
}
}
pcm.skype {
type asym
playback.pcm "skypeout"
capture.pcm "skypein"
}
pcm.skypein {
# Convert from 8-bit unsigned mono (default format set by aoss when
# /dev/dsp is opened) to 16-bit signed stereo (expected by dsnoop)
#
# We cannot just use a "plug" plugin because although the open will
# succeed, the buffer sizes will be wrong and we will hear no sound at
# all.
type route
slave {
pcm "skypedsnoop"
format S16_LE
}
ttable {
0 {0 0.5}
1 {0 0.5}
}
}
pcm.skypeout {
# Just pass this on to the system dmix
type plug
slave {
pcm "dmix"
}
}
pcm.skypedsnoop {
type dsnoop
ipc_key 1133
slave {
# "Magic" buffer values to get skype audio to work
# If these are not set, opening /dev/dsp succeeds but no sound
# will be heard. According to the ALSA developers this is due
# to skype abusing the OSS API.
pcm "hw:0,0"
period_size 256
periods 16
buffer_size 16384
}
bindings {
0 0
}
}
Onwardds, for the sake of test if my sound settings set in pavucontrol enables the internal mic to capture sound I used two programs:
1. gnome-sound-recorder
2. arecord
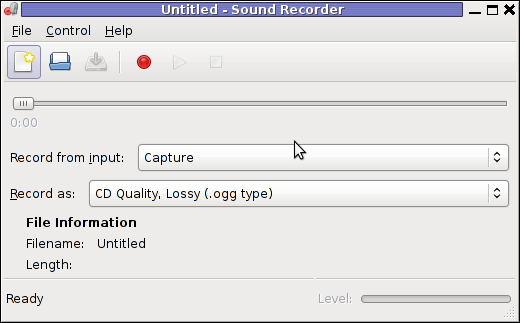
gnome-sound-recorder
gnome-sound-recorder is probably used by most GNOME users, though I'm sure Linux noviced did not play with it yet.
arecord is just a simple console based app to capture sound from the microphone. To test if the microphone works I captured a chunk of sounds with cmd:
debian:~$ arecord cow.wav
Recording WAVE 'cow.wav' : Unsigned 8 bit, Rate 8000 Hz, Mono
Later on I played the file with aplay (part of alsa-utils package in Debian), to check if I'll hear if mic succesfully captured my voice, e.g.:
debian:~$ play cow.wav
cow.wav:
File Size: 22.0k Bit Rate: 64.1k
Encoding: Unsigned PCM
Channels: 1 @ 8-bit
Samplerate: 8000Hz
Replaygain: off
Duration: 00:00:02.75
In:100% 00:00:02.75 [00:00:00.00] Out:22.0k [-=====|=====-] Clip:0
Done.
By the way, the aplay ASCII text equailizer is really awesome 😉 aplay is also capable of playing (Ogg Vorbis .ogg) free sound format.
Further on, I launched the new installed version of skype and tested Skype Calls (Mic capturing), with Skype Echo / Sound Test Service
I'll be glad to hear if this small article, helped anybody to fix any skype Linux related issues ?. I would be happy to hear also from people who had similar issues with a different fixes for skype on Linux.
Its also interesting to hear from Ubuntu and other distributions users if following this tutorial had somehow helped in resolving issues with Skype mic.
Tags: alsa, aptitude, beta, bit, browser windows, Call, card, daily basis, debian gnu, dpkg, emulation, everything, everytime, Flash, GNU, gnu linux, hell, Install, kind of music, Linux, linux experience, linux user, microphone, modern multimedia, modprobe, necessery, nightmare, notebook, proprietary software, reason, rms, sake, Skype, software version, someone, sound card, tabs, upgrade, video
Posted in Linux, Linux and FreeBSD Desktop, Linux Audio & Video, Skype on Linux, Various | No Comments »
How to renew IP address, Add Routing and flush DNS cache on Windows XP / Vista / 7
Friday, November 25th, 2011There are two handy Windows commands which can be used to renew IP address or flush prior cached DNS records which often create problems with resolving hosts.
1. To renew the IP address (fetch address from DHCP server)
C:> ipconfig /release
C:> ipconfig /renew
In above cmd ipconfig /release will de-assign the IP address configured on all Windows LAN and Wireless interfaces, whether ipconfig /renew will send request for IP address to the DNS server.
To unassign and assign again IP address from DHCP server only for a particular LAN or WLAN card:
C:> ipconfig /release LAN
C:> ipconfig /renew LAN
C:> ipconfig /release WLAN
C:> ipconfig /renew WLAN
2. Adding specific routing to Windows
Windows has a Route command similar by syntax to Linux’s route command.
To add routing via a specific predefined IP addresses on Windows the commands should be something like:
C:> Route add 192.168.40.0 mask 255.255.255.0 192.168.41.253
The first command adds IP 192.168.40.0 in the network of 255 hosts to be routed via 192.168.41.253
C:> Route add 0.0.0.0 mask 0.0.0.0 192.168.41.254
The second one adds 192.168.41.254 as a default gateway for all outbound traffic from the Windows host.
To make permanent routing -p switch is used.
3. To clear Windows DNS cache (flush DNS cached records)
C:> ipconfig /flushdns
This will clear all IP records corresponding to hostnames previously cached on the Windows host. Using ipconfig /flushdns is especially handy when IP address for a specific DNS host is changed. Flushing the Windows DNS cache can save us a lot of waiting before the domain example.com starts resolving to the new IP address let’s say 1.2.3.4 instead of the old one 2.2.2.2
Tags: Cache, card, card c, com, command, configured, default gateway, DHCP, DNS, dns host, dns server, domain, domain example, first command, flush dns cache, flushdns, gateway, host, hosts, how to renew ip address, ipconfig, ipconfig flushdns, ipconfig release, mask, network, outbound, outbound traffic, predefined, records c, release c, request, Route, routing, server c, something, switch, unassign, Vista, windows commands, windows lan, WLAN, WLANC
Posted in System Administration, Windows | 1 Comment »
How to install display and audio drivers on motherboard Asus P5B-Plus with video ATI Radeon HD 2600 XT on Windows XP
Wednesday, November 16th, 2011
I re-installed one PC with Windows XP which was refusing to boot. The PC had a hardware of:
Motherboard: Asus P5B-Plus
Video Adapter: ATI Radeon HD 2600 XT
Sound card / Sound Blaster:
Ethernet card: Attansic L1 Gigabit Ethernet 10/100/1000Base-T Controller
It took me like 1 hour of search on the Internet and looking through forum threads and sites to properly install all the hardware. In hope to help someone out there looking to install the hardware Window drivers on ATI RAdeon HD 2600 XT, I’ve made a small archive of all the drivers necessery to make the Video card , Sound Card and Ethernet be properly installed and operating.
Here is download link to all the drivers for ATI Radeon HD 2600 XT to run smoothly on Windows XP
Installation of the drivers on Windows is pretty straight forward download the ATI Radeon HD 2600 XT archive extract and install each one of the files contained in the archive. A few restarts will also be necessery after some of the installed drivers to make the drivers work.
ATI Catalyst (included in the archive) will install the Video drivers for the Radeon XT 2600, whether AD1988AB_Audio_V6585_XpVistaWin7 and 11-11_xp32-64_hdmiaudio will install the Audio drivers. Attansic_L1_Lan_V1737907_V10560011159 contained in the archive needs to be extracted and installed to make the Attensic L1 Gigabit ethernet to show up as installed hardware in Windows device manager.
Hope this post will save some time to ppl looking to install the same drivers on XP 😉
Cheers 😉
Tags: asus p5b, ATI, ati radeon hd 2600, ati radeon hd 2600 xt, audio drivers, Base, card, Catalyst, Cheers, device manager, download, ethernet, forum, forum threads, gigabit ethernet, hardware, hd 2600 xt, Hope, link, manager, necessery, ppl, Radeon, radeon hd 2600, radeon hd 2600 xt, radeon xt, Search, someone, Sound, sound blaster, sound card, time, video, video adapter, video ati, video card, video drivers, window, window drivers, windows xp installation, XPInstallation, XTSound
Posted in System Administration, Windows | No Comments »
How to fix multiple instance music streams with sound card (Intel 82801I ICH9 Family) alsa sound problems on Ubuntu 11.04 GNU / Linux
Thursday, October 27th, 2011
The Ubuntu Linux installed previously on Acer ASPIRE 5736Z on my sisters notebook works quite fine. However today she complained about an issue with her sound. The explanation of the problem she faced is:
When she plays a movie file and pauses it and then switches to a music player, suddenly the notebook sound disappears completely until she restarts all the running programs using the sound server. The Acer Aspire is used with a GNOME Desktop, hence my bet was the issues are most probably caused by some kind of mess happening inside Pulseaudio or the way Alsa loaded kernel drivers handles the multiple sound channel streams.
I’m using GNU / Linux for more than 11 years now and I have faced the same sound issues so many times, so when I heard about the problem I thought its pretty normal.
Anyways, what was really irritating in these situation is that when her laptop sound disappears a video or sound files which are to be played by Mozilla Firefox Browser or Chrome are also loosing the sound.
This causes big issues, especially taking in consideration the fact that she had no idea about computers and is a GUI Desktop user, who have no idea how to restart the pulseaudio server to fix the problem etc.
As a good brother, I took the time to check about the issues related to the specific model of Audio Module Hardware / Sound Card, first I checked the exact model of audio the Acer Aspire 5736Z is equipped with:
stanimiraaaa@Ubuntu-Aspire-5736Z:~$ lspci |grep -i audio
00:1b.0 Audio device: Intel Corporation 82801I (ICH9 Family) HD Audio Controller (rev 03)
I checked about any reported other users issues on the net and I found a user somewhere (lost the link), complaining he is experiencing the same sound oddities on his Acer ASPIRE
The fix he suggested is actually quite simple and comes to adding a simple line to /etc/modprobe.d/alsa-base.conf :
stanimiraaaa@Ubuntu-Aspire-5736Z:~$ sudo su -
[sudo] password for stanimiraaaa:
root@Ubuntu-Aspire-5736Z:~# echo 'options snd_hda_intel model=auto' >> /etc/modprobe.d/alsa-base.conf
Next I restartarted to make the new settings take effect. Its also possible to do it without restart, by unloading and loading the alsa module but I’m a lazy kind of person and the machine is notablyunimportant so why should I bother 😉
One important note here is that I removed also an .asoundrc file, that I created some long time ago and this file might have been creating also some sound issues, the content of ~/.asoundrc, before I delete it in her home user, was like so:
stanimiraaaa@Ubuntu-Aspire-5736Z:~$ cat ~/.asoundrc
pcm.!default {
type hw
card 1
device 0
}
ctl.!default {type hw
card 1
device 0
}
stanimiraaaa@Ubuntu-Aspire-5736Z:~$ rm -f .asoundrc
Doing this minor changes to the Ubuntu system erradicated the sound problems and now the sound with simultaneous sound channel streams works just perfect! Thx God 😉
Tags: alsa, asoundrc, audio controller, bet, card, Chrome, consideration, Desktop, desktop user, exact model, explanation, file, firefox browser, Gnome, gnome desktop, gnu linux, hardware sound, hd, instance, intel corporation, kernel drivers, laptop, mess, modprobe, Module, movie file, Mozilla, music player, music streams, notebook, oddities, player, running programs, sound card, sound files, sound server, sudo, time, type, video
Posted in Everyday Life, Linux, Linux Audio & Video, Various | 2 Comments »
A sysctl Linux variable to change randomly temporary the PC mac address for IPv6 and increase anonymity on IPv6 networks
Tuesday, September 20th, 2011To prevent tracking and increase anonymity in IPv6 networks the Linux kernel has a variable to change randomly the MAC identifier. This feature will be very useful in terms of security in the short future, when all the IPv4 IP addresses are finished. The UIE (Extended Unified Udentifier) for an ipv6 address can be changed with command:
sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.all.use_tempaddr=2
Microsoft Windows Vista and Windows 7 has the UIE enabled by default, enabling the random MAC changes automatically for a host cvan be done as usual by adding the net.ipv6.conf.all_use_tempaddr=2 to /etc/sysctl.conf
On an IPv6 network every ifconfig eth0 down and ifconfig eth0 up will instruct the lan card to be set a different MAC address for the ipv6 ip on the interface.
Changing the UIE randomly however also have security downsides if the host gets infected with a Virus or Worm. The security downsides of the enabled UIE affects mainly Windows hosts on IPv6 networks as UIE variable is enabled by default there.I’ve found this great tip in an article in the latest Linux Magazine October 2011. Its the first time I saw a paper Linux Magazine, the magazine contains a lot of helpful info on the latest Linux developments and latest trends in the Linux world. Subscription to receive the magazine via normal post is for the magazine costs 6.65 EUR per month (80 EUR) yearly. The 80 euro yearly includes 12 CDS (each magazine is bundled with a newly launched new version of a Linux distribution).
There is also a cheaper subscription for the magazine which costs 64.90 EUR.
Tags: anonymity, card, default, distribution, eth, euro, Extended, feature, future, host, hosts, info, ip addresses, ipv6 address, ipv6 network, ipv6 networks, lan card, latest trends, Linux, linux developments, linux distribution, linux kernel, linux magazine, linux world, mac address, Microsoft, microsoft windows vista, month, October, pc mac, Subscription, sysctl, time, tip, UIE, Unified, virus, world subscription, worm
Posted in Linux, System Administration | 2 Comments »




