
Saint Apostle Peter and Paul are the most glorious of all Christ desciples thanks to whom by God's mercy and Grace the nations have received the good news of the Lord Jesus's Christ Crucifix for the sins of all us the sinful people whose evils and unthankfullness is on the way to reach its climax in this days of apostacy where the Church built on top of the Holy Martyrs blood and the Blood and tortures for Christ and the Truth of this two holy man is in one of its biggest temptetation caused by the Coronavirus hysteria exeggerated by the mass-media and purposing to mark a slavery upon human mind and took away the freedoms of man and change the life as we know it.
The Holy Apostles day is the End of the post-Pentecostal fasting which is in the Church from the ancient days of the Church. Rhe date selected being the anniversary of either their death or the translation of their relics.
Fasting is among the 4 main fasts in the One Holy Orthodox Church and the feast in the number of the biggest feasts of the Church. If one reads the historical records for all the places this two simple man was to preach the Gospel he is puzzled and couldn't comprehend how could it be for a simple Roman and a Fisherman to be able to walk through so many lands by boats, ships, through rivers, by carrets, on horses, donkeys, axes, elephants and God knows what kind of other animals typical for the multiple countries and lands this two most holy man has visit.
It is even more amazing that their frutis of faith planted in the nations are still present today in so many Christians through the world …
The saint Peter and Paul fasting has been set for the reason the Apostles, have fasted immediately after Pentecost the descent of the Holy spirit over The desciples of Christ on the 50th day after the Resurrection of the Lord Jesus Christ. The feast has been setup because the Apostles immerse joy of the Holy Spirit who filled their heart spirits, soul and body made them understood how much dirty and how much in sin they and all the humanity is and how much cleanness is necessery in order for them to start their hard mission of spreading the fact of the Resurrection they have witnessed with their own eyes. A small bracket to open here that Saint Paul never had the chance to see in Body the Savior just like Saint Paul and the rest of the Apostles, but he was illuminated by The Lord Jesus Christ's appearance to him on the road of the mask when he was on a journey to hunt for christians and put them to court and to death.
Saint Paul was so fierce (by his zillotism) for the Old Testamental Jewish pharisee faith who was based on human interpretation of God's laws, that he was even physically present on the Killing of Saint Archideacon Stephan.
Saint Paul was the one holding the dresses of the Killers of the first Christian martyr St. Stephan thinking that this devilish deed was truthful and pleasant to God.
But God loved Saint Paul for his Zilotism and his heart aiming to know the Truth and because of that on the Road to Damascus appeared, blinding him from the unbearable light that was emitted by the Lord Jesus Christ who has answered the simple prayer of St. Paul who was honestly looking for the truth. On the Question Saint Paul asked the Unknown bright man who appeared in Glory and surrounded by Angels and Archangels he asked "Who are you Lord"? The reply came, 'I am Jesus, whom you are persecuting'." Acts of the Holy Apostles 9:4-5.
This moment changed Paul forever to make him from a fierce persecutor to a truthful desciple. However as it is said in the Holy Scriptures noone who sees the Lord can't stay alive in the Flesh and perhaps due to that the appearance of Christ left St. Paul to be blind for 3 days until God sent Ananias to heal his eyes by the ordination of Hands in the name of Jesus Christ – again a miracle of God aiming to strengthen the weakness of Faith of Saint Paul and stimulate him to continue on the way of Salvation. Even after the healing of his eyes, later in his eyes by God's providence the eyesight of Paul become weak again and he had to dictate his Apostle letters in the New Testament to his desciples who put it on paper and quite rarely write with his own hand due to his visionary problems. But apperantly the weak physical eye sight doesn't always mean a blindness as with his spiritual eyes the holy apostle was seeing much more than with his physical eyes and one weakness of seeing the physical let him contemplate the eternal.
It is little known fact that saint Paul among with his preaching the Gospel everywhere he went had a profession of making Tents and has worked hardly along with praying day and night, and the sleepless nights of vigil, the tortures by different anti-christians, jews, pagans, philosophers, magicians and others multitude of people who led by his spiritual blindness and passions has done multiple evils and tried in all means to stop Paul to preach the Gospel. But they did not succeeded and we see today the Result as there is rarely a man in the civillized world in all continents who doesn't heard or know about him 20-teen centuries after his martyrdom in the Capital of Roman Empire Rome.

Saint Peter on the other hand was known for his simplicity and he like all of us was suffering of sickness of weakness of faith, he even rejected to know Christ thrice on the Christ trial, even though he was with Christ for the 3.5 years of Christ's preaching his Salvation Way to the world. But again just like with Paul, God made the miracle of preliminary foretelling him the future, warning him that he is about to reject Christ as his teacher a fact that occured just like prophecised by Christ earlier. Saint Peter seeing that The Lord Jesus Christ as the Son of God knows the future believed him and recover his trust in the Resurrection and with repentance came to believe and await the Resurrection of Christ which by the mercy of God he soon saw with his own eys. Soon after this mercy of God and his preparation with the Eyes of Christ and his desires to follow the will of God for his life led him to completely sacrifice all he had in his remaining earthly life for Christ. Saint Peter "Simon" (Σίμων Simōn in Greek), means stone and he is called that way for the fact he become a stone on which the Church of Christ was build and this stone is present their in the Church and everyone in both Christians and not Christians knows him well.

In a dialogue between Jesus and his disciples (Matthew 16:13–19), Jesus asks, "Who do people say that the Son of Man is?" The disciples give various answers. When he asks "Who do you say that I am?", Simon Peter answers, "You are the Messiah, the Son of the living God." Jesus then declares:
Blessed are you, Simon son of Jonah, for this was not revealed to you by flesh and blood, but by my Father in heaven. And I tell you that you are Cephas (Peter) (Petros), and on this rock (petra) I will build my church, and the gates of Hades will not overcome it. I will give you the keys of the kingdom of heaven; whatever you bind on earth will be bound in heaven, and whatever you loose on earth will be loosed in heaven.
Saint Peter is known to have been in Antioch and Corinth and many other lands and is believed to have been the First PopSaint-Apostle-Paul-and-Peter-embrace.jpge of Rome.
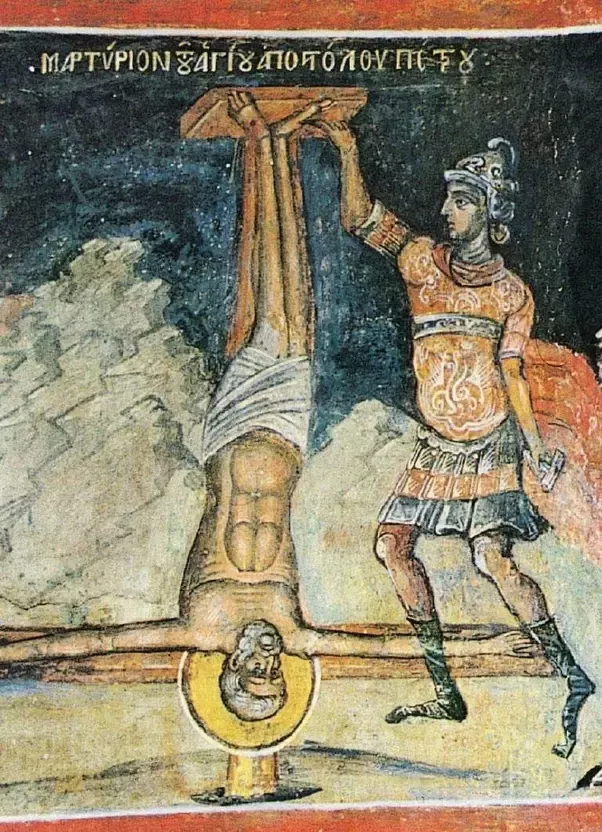

Early Church tradition says that Peter probably died by crucifixion (with arms outstretched) at the time of the Great Fire of Rome in the year 64. This took place three months after the disastrous fire that destroyed Rome for which the emperor (Nero) wished to blame the Christians. This "dies imperii" (regnal day anniversary) was an important one, exactly ten years after Nero ascended to the throne, and it was "as usual" accompanied by much bloodshed. Traditionally, Roman authorities sentenced him to death by crucifixion. In accordance with the apocryphal Acts of Peter, he was crucified head down. Tradition also locates his burial place where the Basilica of Saint Peter was later built, directly beneath the Basilica's high altar.
On the next day 30th of June the Bulgarian Orthodox Church and some of the other Eastern Orthodox Churches celebrate another great feast The Assembly of the 12 Apostles which honors all the 12 Apostles who were the main building blocks whose preach and martyrdom for Christ put the second stones on the Building of the Church which was based on the main base cornerstone Jesus Christ whom with his holy blood for the Salvation of mankind made the existence of the Ship of Salvation (as the holy fathers) call the Church posslble.
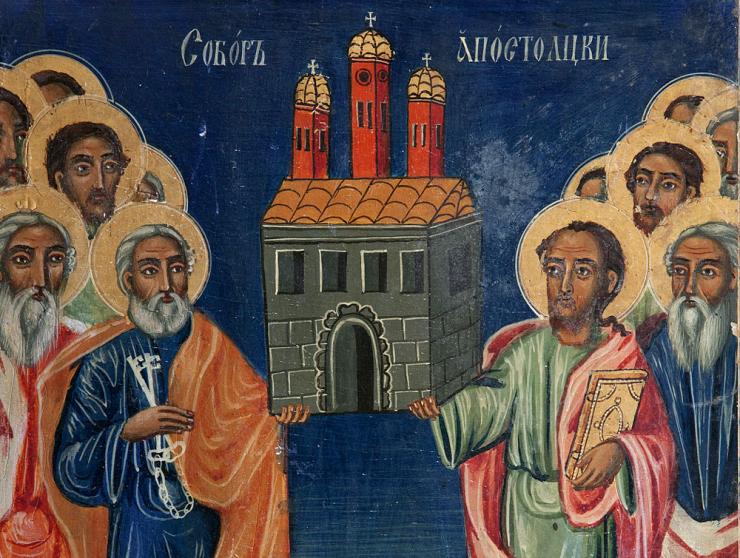

Below are the Church Troparions and Kontaktions (Praising songs in the Church sang in Holy Liturgy) on 29 of June that every year marks Feast of the Glorious Apostles who enlightened the Universe, I put the songs in Both English and in Cyrillic translated out of Old Bulgarian (Church Slavonic).
Here are the names of the 12 Apostles as we know them by Church Tradition
The 12 disciples of Lord Jesus Christ
1. Peter
2. James
3. John
4. Andrew
5. Bartholomew or Nathanael
6. James, the Lesser or Younger
7. Judas
8. Jude or Thaddeus
9. Matthew or Levi
10. Philip
11. Simon the Zealot
12 . Thomas
Troparion — Tone 4
O first-enthroned of the Apostles, / and teachers of the universe, / intercede with the Master of all / to grant peace to the world, / and to our souls great mercy.
Kontakion — Tone 2
O Lord, You have taken to Yourself the steadfast and divinely-inspired heralds, the leaders of Your disciples, / for the enjoyment of Your blessings for and their rest; / for You have accepted their labors and their deaths as above all burnt offerings, / for You alone know the hearts of men.
Kontakion — Tone 2
Today Christ the Rock glorifies with highest honor / the rock of Faith and leader of the Apostles, / together with Paul and the company of the Twelve, / whose memory we celebrate with eagerness of faith, / glorifying Him Who glorified them.
ТРОПАРЬ, ГЛАС 4-Й
Апостолов первопрестольницы и вселенныя учителие, Владыку всех молите мир вселенный даровати и душам нашым велию милость.
Первенствующие из апостолов и Вселенской Церкви учителя, Владыку всех молите мир миру даровать и душам нашим великую милость.
КОНДАК, ГЛАС 2-Й
Твердыя и боговещанныя проповедатели, верх апостолов твоих, Господи, приял еси, в наслаждение благих Твоих и покой: болезни бо онех и смерть приял еси, паче всякаго всеплодия, Едине сведый сердечная.
Непоколебимых и богогласных проповедников, высших из Апостолов Твоих, Господи, Ты принял в наслаждение благ Твоих и покой, ибо страдания их и смерть благоволил принять как жертву, выше всякой жертвы, Единый, ведающий сердца наши.
ВЕЛИЧАНИЕ
Величаем вас, апостоли Христовы Петре и Павле, весь мир ученьми своими просветившия и вся концы ко Христу приведшия.
Прославляем вас, апостолы Христовы Петр и Павел, весь мир своим учением просветивших и приведших ко Христу народы всей земли.
Let by the Prayers of the Holy Apostles Peter and Paul and the Apostle James, John, Andrew, Bartholomew (Nathnael), James (the lesser or Younger), Judas, Jude (Thaddeus), Mathew (Levi), Philip, Simon Zealot and Thomas God have mercy on all Christians in our age and the ages to come till the Second Glorious Coming of Christ and in the Frightening Judgement day.


















No Comments »