If you are a system administrator of a dedicated server and you have no access to Xserver Graphical GNOME / KDE etc. environment and you wonder how you can track the bandwidth connectivity speed of remote system to the internet and you happen to have a modern Linux distribution, here is few ways to do a speedtest.
1. Use speedtest-cli command line tool to test connectivity
speedtest-cli is a tiny tool written in python, to use it hence you need to have python installed on the server.
It is available both for Redhat Linux distros and Debians / Ubuntus etc. in the list of standard installable packages.
a) Install speedtest-cli on Fedora / CentOS / RHEL
On CentOS / RHEL / Scientific Linux lower than ver 8:
$ sudo yum install python
On CentOS 8 / RHEL 8 user type the following command to install Python 3 or 2:
$sudo yum install python3
$ sudo yum install python2
On Fedora Linux version 22+
$ sudo dnf install python
$ sudo dnf install pytho3
Once python is at place download speedtest.py or in case if link is not reachable download mirrored version of speedtest.py on www.pc-freak.net here
$ wget -O speedtest-cli https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sivel/speedtest-cli/master/speedtest.py
$ chmod +x speedtest-cli
Then it is time to run script 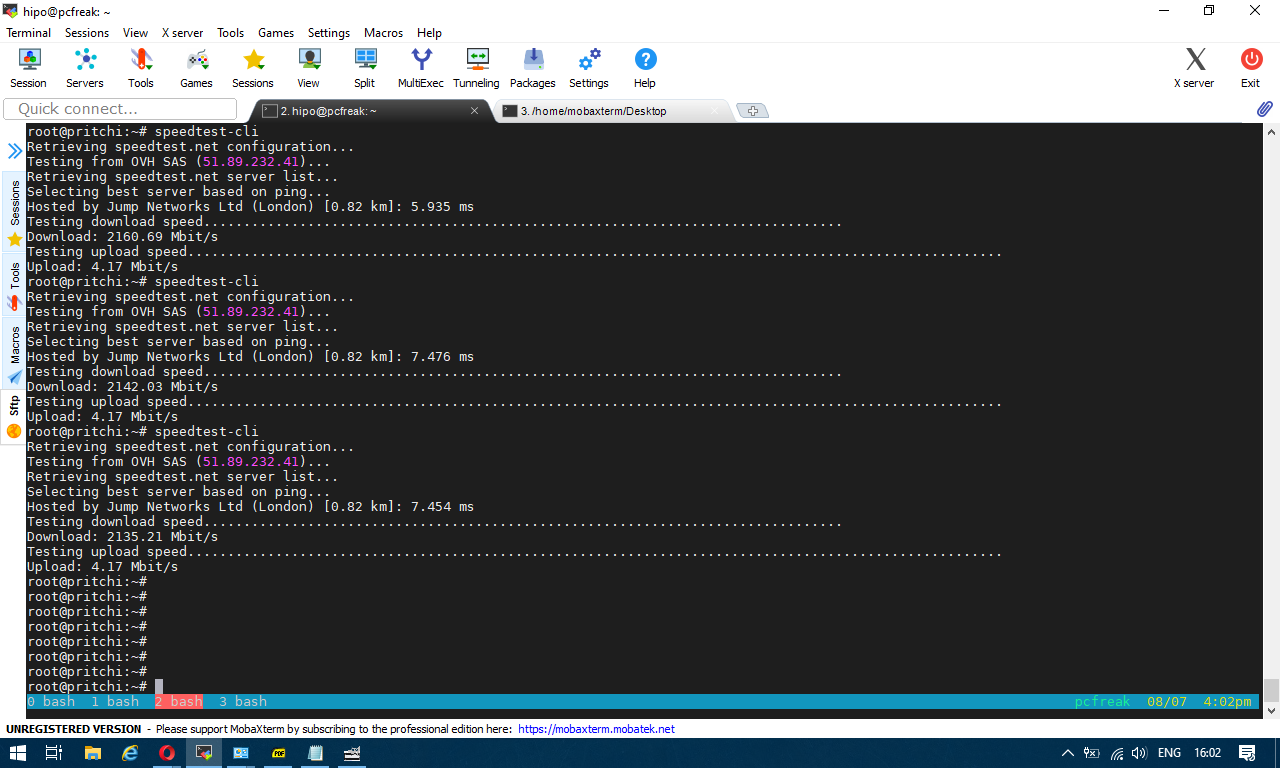
To test enabled Bandwidth on the server
$ python speedtest-cli
b) Install speedtest-cli on Debian
On Latest Debian 10 Buster speedtest is available out of the box in regular .deb repositories, so fetch it with apt
# apt install –yes speedtest-cli
…
You can give now speedtest-cli a try with –bytes arguments to get speed values in bytes instead of bits or if you want to generate an image with test results in picture just like it will appear if you use speedtest.net inside a gui browser, use the –share option
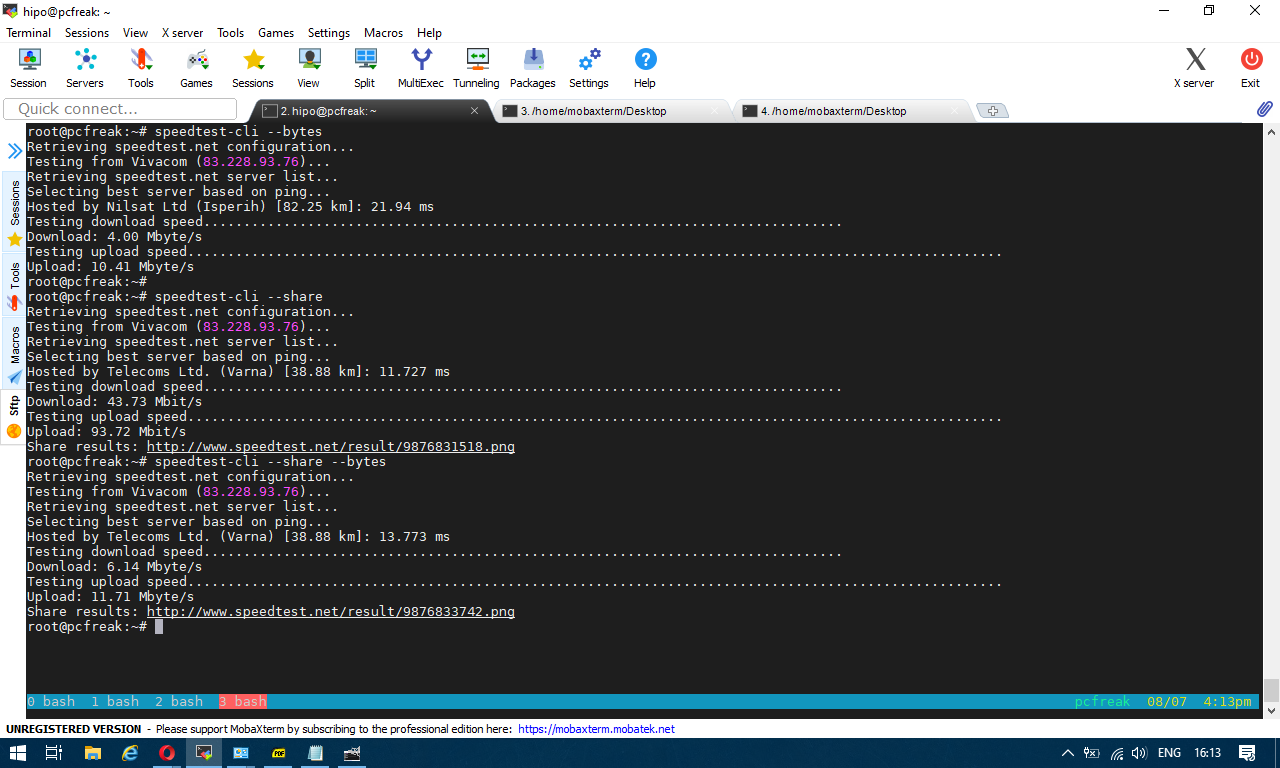
2. Getting connectivity results of all defined speedtest test City Locations
Speedtest has a list of servers through which a Upload and Download speed is tested, to run speedtest-cli to test with each and every server and get a better picture on what kind of connectivity to expect from your server towards the closest region capital cities, fetch speedtest-servers.php list and use a small shell loop below is how:
root@pcfreak:~# wget http://www.speedtest.net/speedtest-servers.php
–2020-08-07 16:31:34– http://www.speedtest.net/speedtest-servers.php
Преобразувам www.speedtest.net (www.speedtest.net)… 151.101.2.219, 151.101.66.219, 151.101.130.219, …
Connecting to www.speedtest.net (www.speedtest.net)|151.101.2.219|:80… успешно свързване.
HTTP изпратено искане, чакам отговор… 301 Moved Permanently
Адрес: https://www.speedtest.net/speedtest-servers.php [следва]
–2020-08-07 16:31:34– https://www.speedtest.net/speedtest-servers.php
Connecting to www.speedtest.net (www.speedtest.net)|151.101.2.219|:443… успешно свързване.
HTTP изпратено искане, чакам отговор… 307 Temporary Redirect
Адрес: https://c.speedtest.net/speedtest-servers-static.php [следва]
–2020-08-07 16:31:35– https://c.speedtest.net/speedtest-servers-static.php
Преобразувам c.speedtest.net (c.speedtest.net)… 151.101.242.219
Connecting to c.speedtest.net (c.speedtest.net)|151.101.242.219|:443… успешно свързване.
HTTP изпратено искане, чакам отговор… 200 OK
Дължина: 211695 (207K) [text/xml]
Saving to: ‘speedtest-servers.php’ speedtest-servers.php 100%[==========================================================================>] 206,73K –.-KB/s in 0,1s
2020-08-07 16:31:35 (1,75 MB/s) – ‘speedtest-servers.php’ saved [211695/211695]
Once file is there with below loop we extract all file defined servers id="" 's
root@pcfreak:~# for i in $(cat speedtest-servers.php | egrep -Eo 'id="[0-9]{4}"' |sed -e 's#id="##' -e 's#"##g'); do speedtest-cli –server $i; done
Retrieving speedtest.net configuration…
Testing from Vivacom (83.228.93.76)…
Retrieving speedtest.net server list…
Retrieving information for the selected server…
Hosted by Telecoms Ltd. (Varna) [38.88 km]: 25.947 ms
Testing download speed……………………………………………………………………..
Download: 57.71 Mbit/s
Testing upload speed…………………………………………………………………………………………
Upload: 93.85 Mbit/s
Retrieving speedtest.net configuration…
Testing from Vivacom (83.228.93.76)…
Retrieving speedtest.net server list…
Retrieving information for the selected server…
Hosted by GMB Computers (Constanta) [94.03 km]: 80.247 ms
Testing download speed……………………………………………………………………..
Download: 35.86 Mbit/s
Testing upload speed…………………………………………………………………………………………
Upload: 80.15 Mbit/s
Retrieving speedtest.net configuration…
Testing from Vivacom (83.228.93.76)…
…..
…
etc.
For better readability you might want to add the ouput to a file or even put it to run periodically on a cron if you have some suspcion that your server Internet dedicated lines dies out to some general locations sometimes.
3. Testing UPlink speed with Download some big file from source location
In the past a classical way to test the bandwidth connectivity of your Internet Service Provider was to fetch some big file, Linux guys should remember it was almost a standard to roll a download of Linux kernel source .tar file with some test browser as elinks / lynx / w3c.
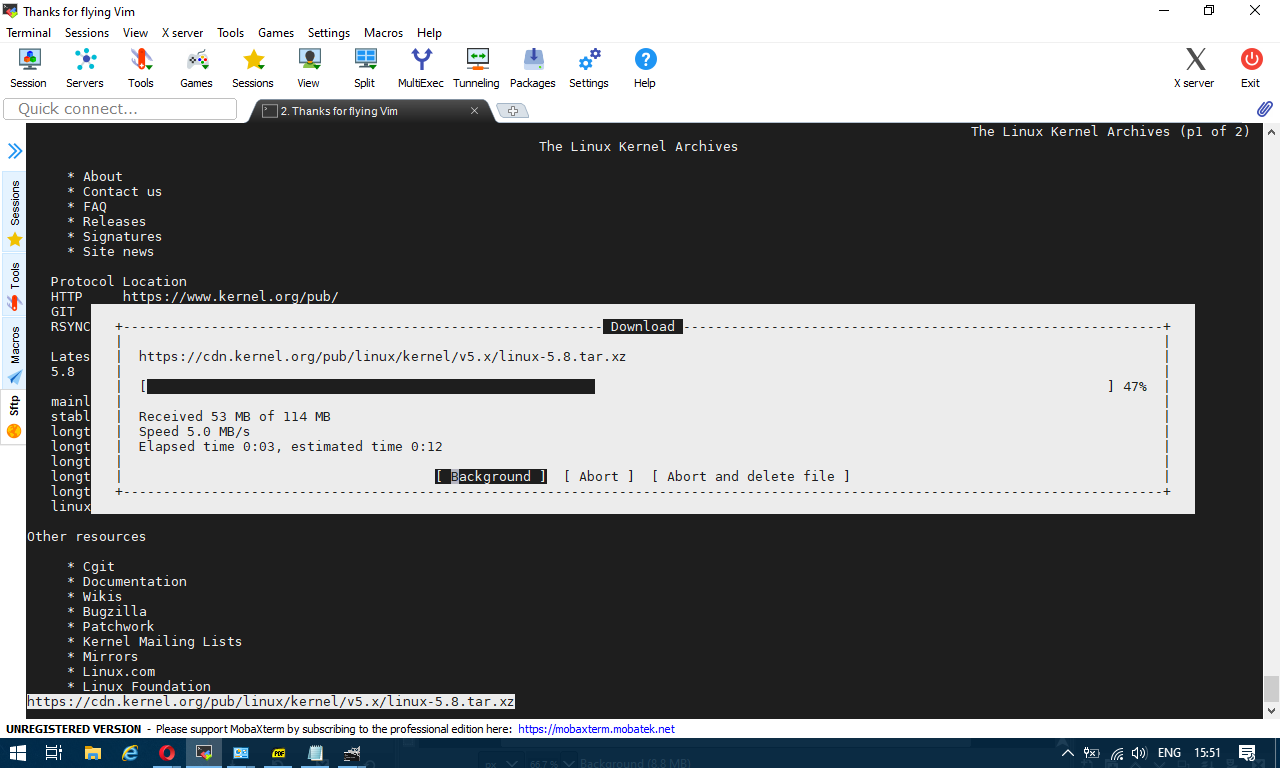
or if those are not at hand test connectivity on remote free shell servers whatever file downloader as wget or curl was used.
Analogical method is still possible, for example to use wget to get an idea about bandwidtch connectivity, let it roll below 500 mb from speedtest.wdc01.softlayer.com to /dev/null few times:
$ wget –output-document=/dev/null http://speedtest.wdc01.softlayer.com/downloads/test500.zip
$ wget –output-document=/dev/null http://speedtest.wdc01.softlayer.com/downloads/test500.zip
$ wget –output-document=/dev/null http://speedtest.wdc01.softlayer.com/downloads/test500.zip
# wget -O /dev/null –progress=dot:mega http://cachefly.cachefly.net/10mb.test ; date
–2020-08-07 13:56:49– http://cachefly.cachefly.net/10mb.test
Resolving cachefly.cachefly.net (cachefly.cachefly.net)… 205.234.175.175
Connecting to cachefly.cachefly.net (cachefly.cachefly.net)|205.234.175.175|:80… connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response… 200 OK
Length: 10485760 (10M) [application/octet-stream]
Saving to: ‘/dev/null’
0K …….. …….. …….. …….. …….. …….. 30% 142M 0s
3072K …….. …….. …….. …….. …….. …….. 60% 179M 0s
6144K …….. …….. …….. …….. …….. …….. 90% 204M 0s
9216K …….. …….. 100% 197M=0.06s
2020-08-07 13:56:50 (173 MB/s) – ‘/dev/null’ saved [10485760/10485760]Fri 07 Aug 2020 01:56:50 PM UTC
To be sure you have a real picture on remote machine Internet speed it is always a good idea to run download of random big files on a certain locations that are well known to have a very stable Internet bandwidth to the Internet backbone routers.
4. Using Simple shell script to test Internet speed
Fetch and use speedtest.sh
wget https://raw.github.com/blackdotsh/curl-speedtest/master/speedtest.sh && chmod u+x speedtest.sh && bash speedtest.sh
5. Using iperf to test connectivity between two servers
iperf is another good tool worthy to mention that can be used to test the speed between client and server.
To use iperf install it with apt and do on the server machine to which bandwidth will be tested:
# iperf -s
On the client machine do:
# iperf -c 192.168.1.1
where 192.168.1.1 is the IP of the server where iperf was spawned to listen.
6. Using Netflix fast to determine Internet connection speed on host
Fast
fast is a service provided by Netflix. Its web interface is located at Fast.com and it has a command-line interface available through npm (npm is a package manager for nodejs) so if you don't have it you will have to install it first with:
# apt install –yes npm
Note that if you run on Debian this will install you some 249 new nodejs packages which you might not want to have on the system, so this is useful only for machines that has already use of nodejs.
$ fast
82 Mbps ↓
The command returns your Internet download speed. To get your upload speed, use the -u flag:
$ fast -u
⠧ 80 Mbps ↓ / 8.2 Mbps ↑
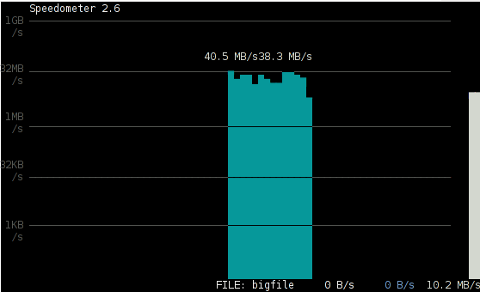
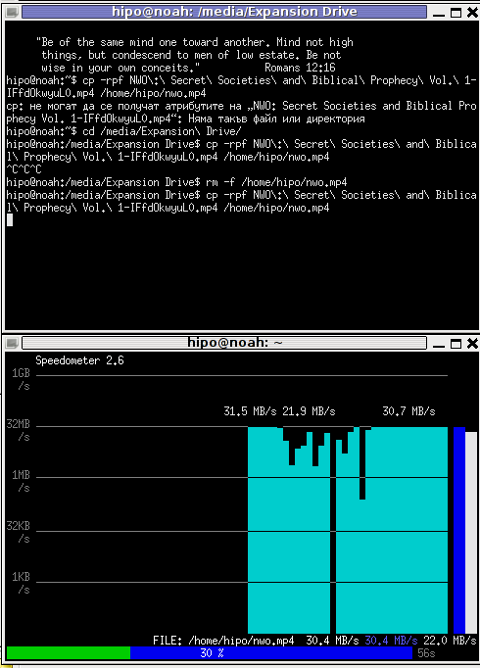
7. Use speedometer / iftop to measure incoming and outgoing traffic on interface
If you're measuring connectivity on a live production server system, then you might consider that the measurement output might not be exactly correct especially if you're measuring the Uplink / Downlink on a Heavy loaded webserver / Mail Server / Samba or DNS server.
If this is the case a very useful tools to consider to extract the already taken traffic used on your Incoming and Outgoing ( TX / RX ) Network interfaces are speedometer and iftop, they're present and installable depending on the OS via yum / apt or the respective package manager.
To install on Debian server:
# apt install –yes iftop speedometer
The most basic use to check the live received traffic in a nice Ncurses like text graphic is with:
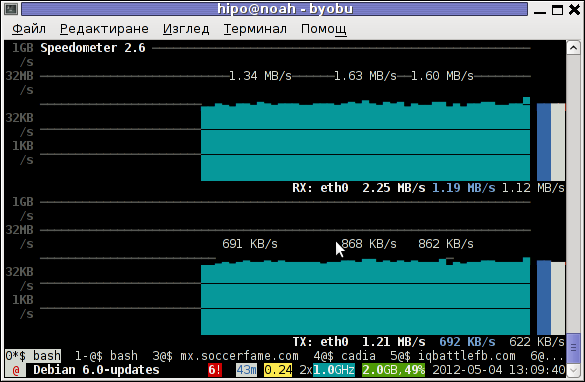
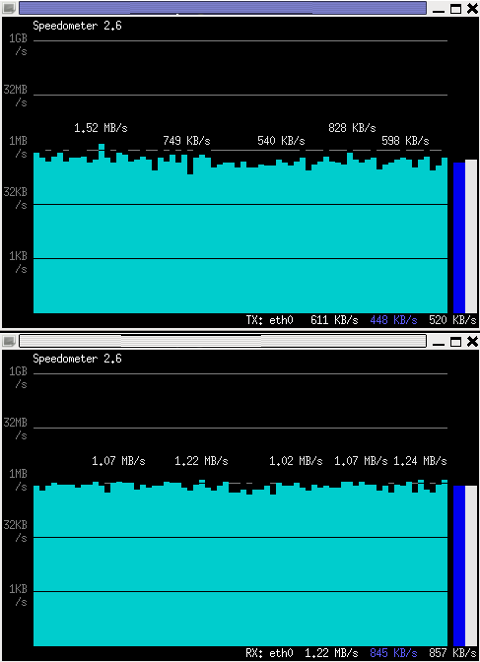
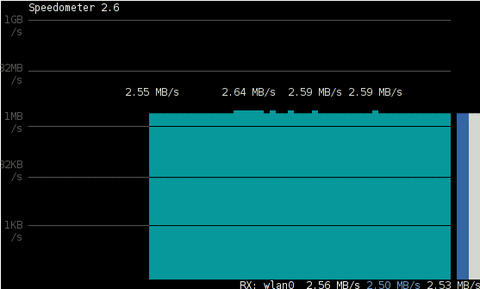
# speedometer -r
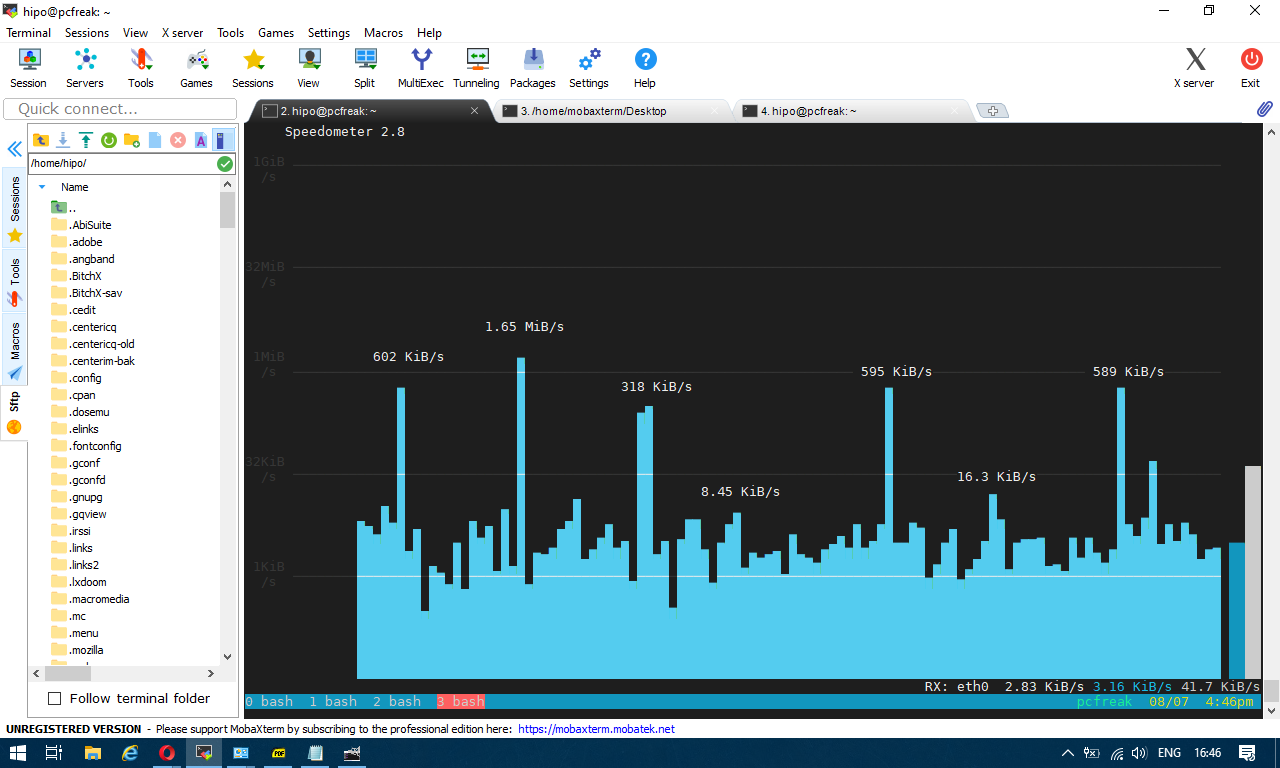
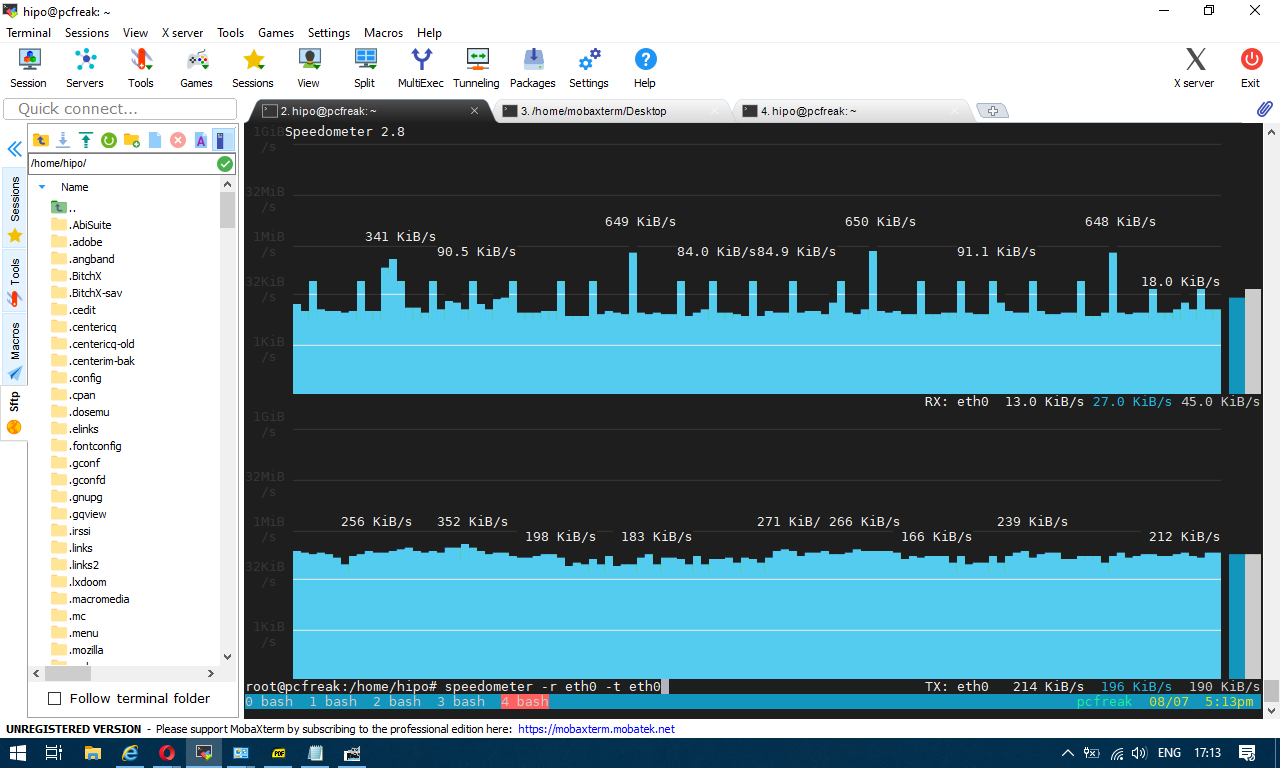
To generate real time ASCII art graph on RX / TX traffic do:
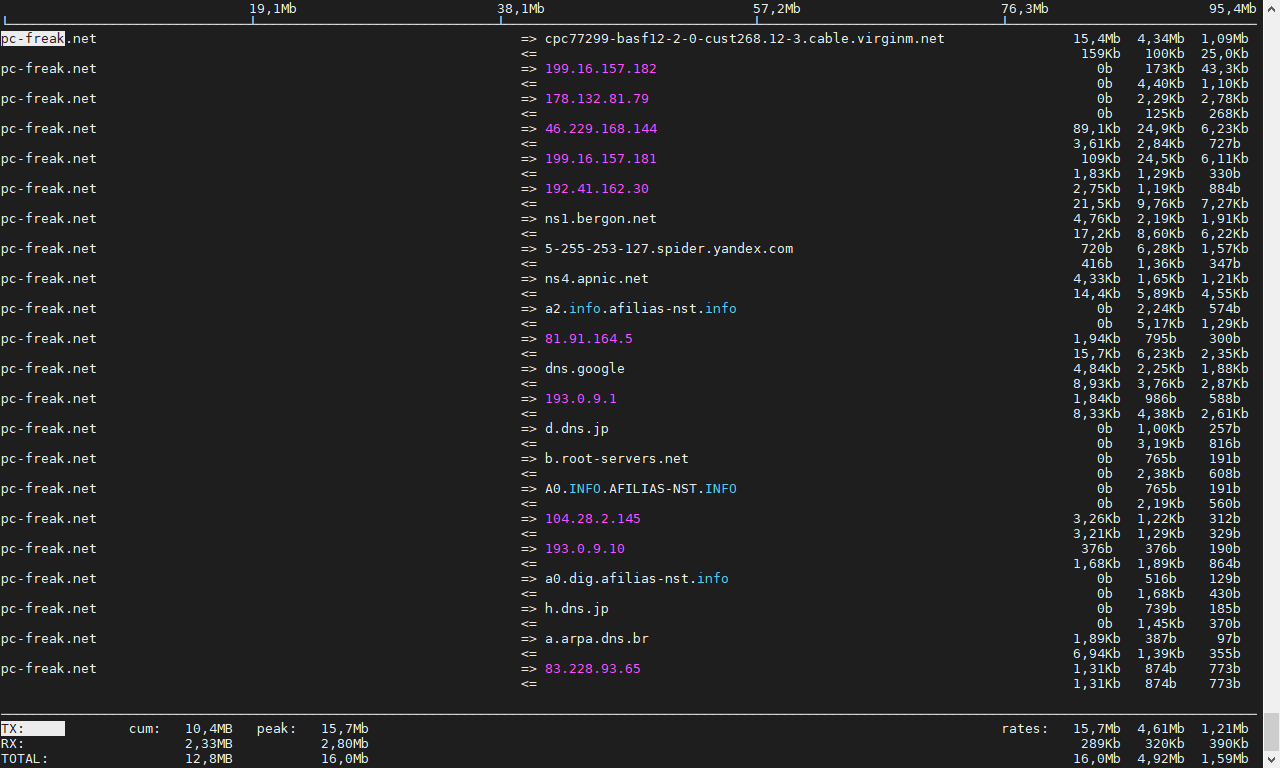
# speedometer -r eth0 -t eth0
# iftop -P -i eth0