There two main reasons which cause incorrect clock settings on Slackware Linux.
One common reason for incorrectly set time is improper clock and timezone settings during Slackware install.
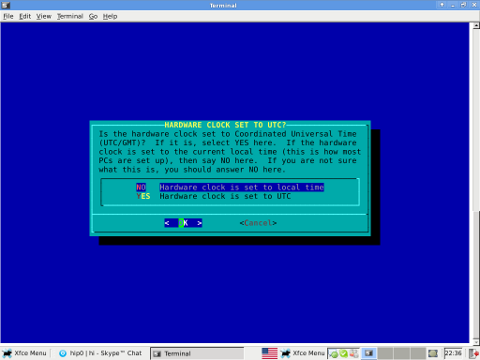
On install, one of the ncruses install menus asks an ambigious dialog question reading
HARDWARE CLOCK SET TO UTC?
Is the hardware clock set to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC/GMT)?
Some newbie Slackware users make the mistake to choose YES here, resulting in incorrectly set clock.
Second possibility for improper time is incorrect time on BIOS level. This is not so common among laptop and modern desktop PCs. However in the past impoper system BIOS hardware clock was usual.
In any case it is a good practice to check the system PC BIOS clock settings.
To check BIOS battery hardware clock from command line use:
bash-4.1# hwclock --show
Fri 24 Feb 2012 01:24:18 AM EET -0.469279 seconds
The system clock on Slackware is set via a script called timeconfig. To fix slack's incorrect host time run:
bash-4.1# timeconfig
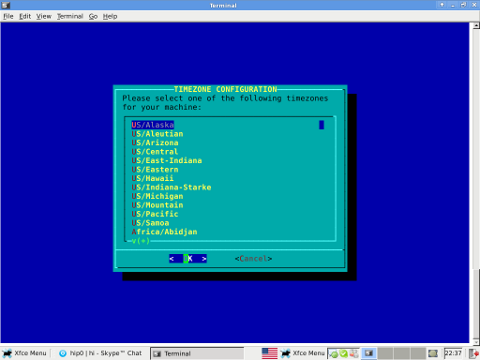
Running timeconfig once should configure a proper timezone to be set on next system reboot, however the system time will probably still be not ok.
To manually set time to right time, use date command. To set manually the system wide time to 12:00:00 with date:
bash-4.1# date -s "12:00:00"
Anyways for time accuracy the ntpdate should be used to feth time from NTP internet time server:
bash-4.1# ntpdate time.nist.gov
...
Finally to make the new set right time permanent also for the BIOS battery clock issue:
bash-4.1# hwclock --systohc
By the way its curious fact Slackware Linux is the oldest still existent GNU / Linux based distribution. Its up and running since the very day GNU and Linux came to merge at one Free OS 😉